Organic chemistry: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:5-alpha-dihydroprogesterone.png|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:5alpha-Dihydroprogesterone_3D_ball.png|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:5alpha-Dihydroprogesterone_3D_spacefill.png|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Friedrich_woehler.jpg|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Grubbs-1G-from-xtal-2010-3D-balls.png|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Cyanocobalamin.svg|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:OrgNom.svg|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Stuctural_drawings_of_butane_854px.jpg|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Acetic_acid_atoms.svg|Organic_chemistry | |||
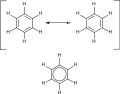
File:Benzene-resonance-structures.svg|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Girl_with_swimming_board.jpg|Organic_chemistry | |||
File:Maitotoxin_2D_structure.svg|Organic_chemistry | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:15, 18 February 2025
Organic chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that studies the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and synthesis of organic compounds, which contain carbon atoms. Organic compounds are structurally diverse and numerous because of the capacity of carbon to form strong bonds with other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. Organic chemistry is primarily concerned with carbon-containing compounds, including hydrocarbons and their derivatives.
History[edit]
Friedrich Wöhler is often credited with being the "father" of organic chemistry. In 1828, Wöhler synthesized urea, an organic compound found in urine, from inorganic starting materials, in what is now called the Wöhler synthesis. This discovery overturned the prevailing belief of the time that organic compounds could only be obtained from living organisms through vitalism.
Branches of Organic Chemistry[edit]
Organic chemistry can be divided into several major areas:
- Physical organic chemistry is the study of the relationship between structure and reactivity of organic molecules.
- Bioorganic chemistry combines organic chemistry and biochemistry.
- Organometallic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon–metal bonds.
- Polymer chemistry involves the study of the chemistry of polymers.
- Medicinal chemistry is focused on drug discovery and development.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />