Trustee: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Trustee == | |||
A ''' | A '''trustee''' is an individual or organization that holds or manages and invests assets for the benefit of another. Trustees are often appointed to manage the assets of a [[trust]], which is a legal arrangement in which one party, known as the [[trustor]], gives another party, the trustee, the right to hold title to property or assets for the benefit of a third party, the [[beneficiary]]. | ||
[[File:Chart_of_a_trust.jpg|thumb|right|A chart illustrating the structure of a trust.]] | |||
== Responsibilities == | |||
Trustees have a [[fiduciary duty]] to manage the trust's assets in the best interests of the beneficiaries. This includes making prudent investment decisions, ensuring that the trust's assets are protected, and distributing income or principal according to the terms of the trust document. Trustees must act impartially, balancing the interests of all beneficiaries, and must avoid conflicts of interest. | |||
== Types of Trustees == | == Types of Trustees == | ||
Trustees can be individuals or [[corporate trustee|corporate entities]]. | |||
* ''' | * '''Individual Trustees''': These are often family members or close friends of the trustor. They are chosen for their personal relationship with the trustor and their understanding of the trustor's wishes. | ||
* ''' | |||
* '''Corporate Trustees''': These are professional entities, such as banks or trust companies, that provide trustee services for a fee. They are chosen for their expertise in managing trusts and their ability to provide continuity and impartiality. | |||
== Appointment and Removal == | |||
Trustees are typically appointed by the trustor in the trust document. The document may also specify the process for removing a trustee and appointing a successor. In some cases, beneficiaries or a court may have the power to remove a trustee if they fail to fulfill their duties. | |||
== Legal Framework == | == Legal Framework == | ||
The | The role and responsibilities of trustees are governed by [[trust law]], which varies by jurisdiction. In many places, trustees are subject to statutory duties, such as the duty to act in good faith and the duty to account to beneficiaries. | ||
== | == Related Pages == | ||
* [[Trust law]] | * [[Trust law]] | ||
* [[Fiduciary]] | * [[Fiduciary]] | ||
* [[Beneficiary]] | * [[Beneficiary]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Trustor]] | ||
[[Category:Trust law]] | [[Category:Trust law]] | ||
Revision as of 11:57, 9 February 2025
Trustee
A trustee is an individual or organization that holds or manages and invests assets for the benefit of another. Trustees are often appointed to manage the assets of a trust, which is a legal arrangement in which one party, known as the trustor, gives another party, the trustee, the right to hold title to property or assets for the benefit of a third party, the beneficiary.
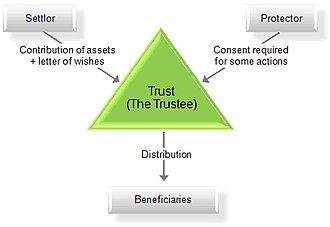
Responsibilities
Trustees have a fiduciary duty to manage the trust's assets in the best interests of the beneficiaries. This includes making prudent investment decisions, ensuring that the trust's assets are protected, and distributing income or principal according to the terms of the trust document. Trustees must act impartially, balancing the interests of all beneficiaries, and must avoid conflicts of interest.
Types of Trustees
Trustees can be individuals or corporate entities.
- Individual Trustees: These are often family members or close friends of the trustor. They are chosen for their personal relationship with the trustor and their understanding of the trustor's wishes.
- Corporate Trustees: These are professional entities, such as banks or trust companies, that provide trustee services for a fee. They are chosen for their expertise in managing trusts and their ability to provide continuity and impartiality.
Appointment and Removal
Trustees are typically appointed by the trustor in the trust document. The document may also specify the process for removing a trustee and appointing a successor. In some cases, beneficiaries or a court may have the power to remove a trustee if they fail to fulfill their duties.
Legal Framework
The role and responsibilities of trustees are governed by trust law, which varies by jurisdiction. In many places, trustees are subject to statutory duties, such as the duty to act in good faith and the duty to account to beneficiaries.