Wavelength: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category:Wave theory]] | [[Category:Wave theory]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Sine_wavelength.svg|Wavelength | |||
File:Waves_in_Box.svg|Wavelength | |||
File:Standing_wave_2.gif|Wavelength | |||
File:Wavelength_&_refractive_index.JPG|Wavelength | |||
File:Refraction_-_Huygens-Fresnel_principle.svg|Wavelength | |||
File:Light_dispersion_conceptual_waves.gif|Wavelength | |||
File:Local_wavelength.svg|Wavelength | |||
File:Cochlea_wave_animated.gif|Wavelength | |||
File:Wavelength_indeterminacy.JPG|Wavelength | |||
File:Periodic_waves_in_shallow_water.png|Wavelength | |||
File:Nonsinusoidal_wavelength.svg|Wavelength | |||
File:Wave_packet_(dispersion).gif|Wavelength | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:49, 18 February 2025
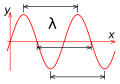
Wavelength is a term used in Physics and Wave theory to describe the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns.
Introduction[edit]
The term wavelength is derived from the concept of a wave of light or sound. It is the distance between one peak or crest of a wave and the next peak or crest. It is often measured in metres (m), centimetres (cm), or nanometres (nm) for light waves, and in hertz (Hz) for sound waves.
Mathematical representation[edit]
The wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). In mathematical terms, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns.
Wavelength and frequency[edit]
The relationship between wavelength and frequency for a wave is given by the equation:
v = fλ
where: v is the speed of the wave (also known as the phase speed), f is the frequency of the wave, and λ is the wavelength of the wave.
This equation can be rearranged to find the wavelength of a wave:
λ = v/f
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />