Temporal lobe: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray730.png | |||
File:Temporal_lobe_animation.gif | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 17 February 2025
Temporal lobe
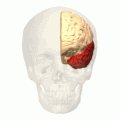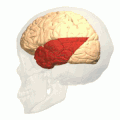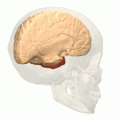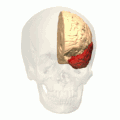
The Temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral sulcus and at roughly the same level as the ear. It plays a key role in processing sensory input and assigning it emotional meaning. It is also involved in visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association.
Anatomy[edit]
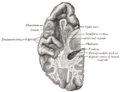
The temporal lobe is located on the side of the brain, beneath the lateral fissure. It is divided into two main areas: the superior temporal gyrus, which includes the primary auditory cortex, and the inferior temporal gyrus, which includes the primary visual cortex.
Function[edit]
The temporal lobe is involved in several functions of the body including auditory perception, memory, and speech. It is also responsible for processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association.
Auditory perception[edit]
The primary auditory cortex is responsible for the processing of sounds. Specific sound frequencies are processed in specific regions of the auditory cortex.
Memory[edit]
The temporal lobe is critical for memory. The hippocampus, located in the temporal lobe, is particularly important in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory.
Speech[edit]
The temporal lobe is involved in the processing of semantics in both speech and vision. The Wernicke's area, located in the superior temporal gyrus in the dominant cerebral hemisphere, which is the left hemisphere in about 95% of right-handed individuals and 70% of left-handed individuals, is responsible for the comprehension of speech.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the temporal lobe can result in a variety of disorders including auditory agnosia, Wernicke's aphasia, amnesia, and Alzheimer's disease.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />