Lever: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Lever_Principle_3D.png|Lever Principle in 3D | |||
File:Lever_(PSF).png|Illustration of a Lever | |||
File:Levers_of_the_Human_Body.svg|Levers of the Human Body | |||
File:Archimedes_lever_(Small).jpg|Archimedes' Lever | |||
File:Seesaw1902.jpg|Seesaw from 1902 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:05, 18 February 2025
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or fulcrum. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists drawing from Greek texts on technology.
Principle of levers[edit]
The principle of levers, also known as the law of the lever, states that the distance from the fulcrum to the point of effort is inversely proportional to the distance from the fulcrum to the point of resistance. This principle is used to determine the mechanical advantage of the lever.
Types of levers[edit]
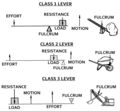
There are three classes of levers, depending on the relative positions of the fulcrum, the load and the effort.
First-class levers[edit]
In a first-class lever, the fulcrum is located between the effort and the load. Examples of first-class levers include seesaws, crowbars, and pliers.
Second-class levers[edit]
In a second-class lever, the load is located between the effort and the fulcrum. Examples of second-class levers include wheelbarrows, nutcrackers, and bottle openers.
Third-class levers[edit]
In a third-class lever, the effort is located between the load and the fulcrum. Examples of third-class levers include tweezers, brooms, and the human arm.
Applications of levers[edit]
Levers are used in a wide variety of applications, from simple tools to complex machinery. They are used to amplify an input force, change the direction of a force, or increase the speed or distance of a force.