Glottis: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Arytenoid_cartilage.png|Arytenoid cartilage | |||
File:Glottis_positions.png|Glottis positions | |||
File:Illu07_larynx01.jpg|Larynx illustration | |||
File:Gray955.png|Glottis | |||
File:Gray1204.png|Glottis | |||
File:Slide7vvv.JPG|Glottis | |||
File:Slide1kuku.JPG|Glottis | |||
File:Slide2kuku.JPG|Glottis | |||
File:Slide3kuku.JPG|Glottis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:24, 18 February 2025
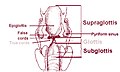
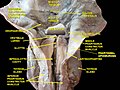
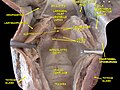
Glottis is the part of the larynx consisting of the vocal cords and the opening between them. It affects voice modulation through expansion or contraction.
Anatomy[edit]
The glottis is located in the middle part of the larynx between the open part of the larynx and the vocal folds. The size of the glottis is changeable. It is wide open during inhalation, but closes during the production of speech or when swallowing.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the glottis is related to speech production, breathing, and swallowing. It plays a crucial role in the production of voiced and voiceless consonants in many languages, and it is also the part of the larynx that is most often affected in laryngeal diseases and disorders.
Diseases and Disorders[edit]
There are several diseases and disorders that can affect the glottis, including:
- Laryngitis: This is an inflammation of the larynx, which can cause the glottis to swell and result in a hoarse voice or loss of voice.
- Glottic cancer: This is a type of throat cancer that originates in the glottis. It is often associated with smoking and heavy alcohol use.
- Vocal cord paralysis: This is a condition where one or both of the vocal cords cannot move. It can result in a soft voice, voice changes, or difficulty breathing.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for diseases and disorders of the glottis depends on the specific condition and its severity. Treatments may include medication, voice therapy, or surgery. In some cases, a tracheostomy may be necessary.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />