Frenulum: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
[[Category:Digestive system]] | [[Category:Digestive system]] | ||
[[Category:Genital anatomy]] | [[Category:Genital anatomy]] | ||
== Frenulum == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray1202.png|Gray1202 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:30, 23 February 2025
Frenulum is a small fold of tissue that secures or restricts the motion of a mobile organ in the body. There are several frenula in different parts of the human body, such as those found in the mouth, digestive tract, and genitals.
Anatomy[edit]
The term "frenulum" is derived from the Latin word "frenum," which means "bridle." In the human body, a frenulum is a fold of tissue or muscle that supports an organ or structure, keeps it in place, and restricts its movement to a certain extent.
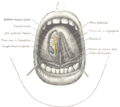
Oral Frenula[edit]
In the mouth, there are three frenula:
- The lingual frenulum under the tongue.
- The labial frenulum attaching the inside of the upper lip to the gums.
- The inferior labial frenulum attaching the inside of the lower lip to the gums.
Digestive Tract Frenula[edit]
In the digestive tract, there are two frenula:
- The frenulum of ileocecal valve in the gastrointestinal tract.
- The frenulum of appendix in the gastrointestinal tract.
Genital Frenula[edit]
In the genitals, there are three frenula:
- The frenulum of prepuce of penis in males.
- The frenulum of labia minora in females.
- The frenulum of clitoris in females.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The frenulum can sometimes be the site of certain medical conditions. For example, a short lingual frenulum (a condition known as ankyloglossia or "tongue-tie") can cause speech difficulties and problems with breastfeeding in infants. Similarly, a short frenulum of the penis can cause discomfort during sexual activities.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />