Hemiazygos vein: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Hemiazygos_vein == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray480.png|Gray480 | |||
File:Gray577.png|Gray577 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:00, 23 February 2025
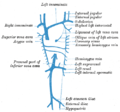
Hemiazygos vein is a vein running vertically in the lower thoracic region, which can be found on the left side of the vertebral column. It plays a crucial role in the human circulatory system, particularly in draining the thoracic and abdominal walls. The hemiazygos vein is part of the azygos system, which is a network of veins located on either side of the thoracic vertebral column.
Anatomy[edit]
The hemiazygos vein begins in the left ascending lumbar vein or the left renal vein. It ascends along the left side of the vertebral column, crossing over at the level of the eighth thoracic vertebra to join the azygos vein. The hemiazygos vein receives tributaries corresponding to the posterior intercostal veins and the left bronchial vein.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the hemiazygos vein is to drain blood from the thoracic and abdominal walls. It does this by receiving blood from the left subcostal and ascending lumbar veins, as well as the lower posterior intercostal veins. The hemiazygos vein then transports this blood to the azygos vein, which carries it to the superior vena cava and then to the heart.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The hemiazygos vein can be affected by various medical conditions. For instance, it can become enlarged in cases of superior vena cava syndrome, a condition where the superior vena cava is obstructed. This can lead to the development of collateral circulation, where blood flow is rerouted through smaller veins.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />