Dissociative disorder: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
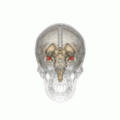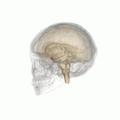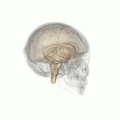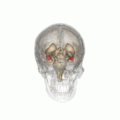
File:Amygdala_small.gif|Amygdala | |||
File:Hippocampus_small.gif|Hippocampus | |||
File:Prefrontal_cortex_(left)_animation.gif|Prefrontal cortex (left) | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:29, 18 February 2025
Dissociative Disorder is a mental health condition that involves disruptions or breakdowns of memory, awareness, identity, or perception. People with the disorder use dissociation, a defense mechanism, pathologically and involuntarily. Dissociative disorders are thought to primarily be caused by psychological trauma.
Symptoms
The symptoms of dissociative disorders depend on the type of disorder that has been diagnosed. There are three types of dissociative disorders defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM): Dissociative Amnesia, Dissociative Identity Disorder, and Depersonalization Disorder.
Dissociative Amnesia
The main symptom is difficulty remembering important information about one’s self. Dissociative amnesia may surround a particular event, such as combat or abuse, or more rarely, information about identity and life history.
Dissociative Identity Disorder
Formerly known as Multiple Personality Disorder, this disorder is characterized by "switching" to alternate identities. You may feel the presence of two or more people talking or living inside your head, and you might feel as though you're possessed by other identities.
Depersonalization Disorder
This disorder involves ongoing feelings of being detached or disconnected from one’s self, observing oneself from an outside perspective, or experiences of unreality, numbness or altered sensations.
Causes
Dissociative disorders usually develop as a way to cope with trauma. The disorders most often form in children subjected to long-term physical, sexual or emotional abuse or, less often, a home environment that's frightening or highly unpredictable. The stress of war or natural disasters also can bring on dissociative disorders.
Treatment
Psychotherapy is the primary treatment for dissociative disorders. This form of therapy, also known as talk therapy, counseling or psychosocial therapy, involves talking about your disorder and related issues with a mental health professional. Other treatments include cognitive and creative therapies.