Crossbite: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Crossbite == | |||
<gallery> | |||
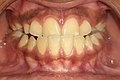
File:crossbite.jpg|Crossbite | |||
File:Class_1_with_anterior_crossbite.jpg|Class 1 with anterior crossbite | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 20:55, 23 February 2025
Crossbite is a type of malocclusion where the upper and lower teeth do not align properly. It can affect a single tooth or a group of teeth and can occur on either or both sides of the mouth. Crossbite can be classified into two types: anterior crossbite and posterior crossbite.
Types of Crossbite
Anterior Crossbite
An Anterior Crossbite occurs when the upper front teeth sit behind the lower front teeth when the mouth is closed. This is also known as an underbite.
Posterior Crossbite
A Posterior Crossbite occurs when the upper back teeth sit inside the lower back teeth when the mouth is closed.
Causes of Crossbite
Crossbite is usually caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the common causes include:
- Genetics
- Delayed or abnormal tooth eruption
- Thumb sucking or prolonged use of a pacifier
- Mouth breathing
- Jaw trauma
Treatment of Crossbite
The treatment for crossbite depends on the type and severity of the condition. Treatment options include:
Complications of Crossbite
If left untreated, crossbite can lead to various complications such as: