Medial medullary syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
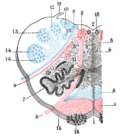
File:Gray700.png|Medial medullary syndrome | |||
File:Human_brainstem_blood_supply_description.JPG|Medial medullary syndrome | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:47, 18 February 2025
Medial Medullary Syndrome (also known as Dejerine Syndrome) is a type of stroke that affects the medulla oblongata, a part of the brainstem. This condition is typically caused by a blockage in the anterior spinal artery, which supplies blood to the medulla.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Medial Medullary Syndrome can vary depending on the severity and location of the stroke. Common symptoms include:
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body (hemiparesis)
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing (dysarthria and dysphagia)
- Loss of sensation on the opposite side of the body
- Vertigo or dizziness
- Nystagmus, an involuntary movement of the eyes
Causes
The primary cause of Medial Medullary Syndrome is a blockage in the anterior spinal artery. This can occur due to a variety of reasons, including:
- Atherosclerosis, a condition where the arteries become narrow due to the buildup of plaque
- Blood clots
- Inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis)
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Medial Medullary Syndrome is typically made based on the patient's symptoms and medical history. Imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI may be used to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the stroke.
Treatment
Treatment for Medial Medullary Syndrome focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing further strokes. This may include:
- Medications to control blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots
- Physical therapy to help with mobility and strength
- Speech therapy to help with speech and swallowing difficulties
Prognosis
The prognosis for Medial Medullary Syndrome can vary greatly depending on the severity of the stroke and the patient's overall health. Some people may make a full recovery, while others may have long-term or permanent disabilities.