Medial plantar nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray357.png|Medial plantar nerve | |||
File:Gray834.svg|Medial plantar nerve | |||
File:Gray836.png|Medial plantar nerve | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:53, 18 February 2025
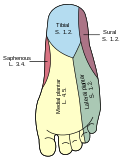
Medial Plantar Nerve is a branch of the tibial nerve, which is itself a branch of the sciatic nerve. The medial plantar nerve is responsible for the innervation of the skin and muscles of the medial part of the foot.
Anatomy[edit]
The medial plantar nerve originates from the tibial nerve in the foot. It travels along the medial side of the foot, providing sensory and motor innervation to various structures. It is comparable to the median nerve of the hand in terms of its distribution.
Function[edit]
The medial plantar nerve has both sensory and motor functions. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the medial part of the sole of the foot, the medial three and a half toes, and the associated joint capsules and skin. It provides motor innervation to the abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis, and the first lumbrical.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Damage to the medial plantar nerve can result in loss of sensation in the medial part of the sole and the medial three and a half toes. It can also cause weakness in the muscles it innervates, leading to difficulties in walking and maintaining balance.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />