Hypervascularity: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
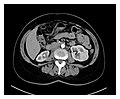
File:Preoperative-contrasted-CT-scans-of-the-patient-showing-multiple-bilateral-kidney-tumors-with-diameters-ranging-between.jpg|Preoperative contrasted CT scans of the patient showing multiple bilateral kidney tumors with diameters ranging between | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:01, 17 February 2025
Hypervascularity refers to an increased number of blood vessels in a particular area of the body. This condition can be a sign of various diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and certain types of infections. Hypervascularity is often detected through imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
Causes of Hypervascularity[edit]
Hypervascularity can be caused by a variety of conditions, including:
- Cancer: Many types of cancer can cause hypervascularity as the tumor grows and requires more blood supply.
- Inflammation: Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can cause hypervascularity in the affected areas.
- Infections: Certain types of infections can cause hypervascularity as the body increases blood flow to fight off the infection.
Diagnosis of Hypervascularity[edit]
Hypervascularity is often detected through imaging studies. These may include:
- Ultrasound: This imaging study uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It can detect increased blood flow in an area, which may indicate hypervascularity.
- CT scan: This imaging study uses X-rays to create detailed images of the inside of the body. It can detect changes in the structure of blood vessels that may indicate hypervascularity.
- MRI: This imaging study uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the body. It can detect changes in the structure and function of blood vessels that may indicate hypervascularity.
Treatment of Hypervascularity[edit]
The treatment of hypervascularity depends on the underlying cause. For example, if hypervascularity is caused by cancer, treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. If it is caused by an inflammatory condition, treatment may involve anti-inflammatory medications or other therapies to manage the inflammation.