Orbitofrontal cortex: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:Cognitive neuroscience]] | [[Category:Cognitive neuroscience]] | ||
[[Category:Frontal lobe]] | [[Category:Frontal lobe]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:MRI_of_orbitofrontal_cortex.jpg|MRI of orbitofrontal cortex | |||
File:Gray729_orbital_gyrus.png|Gray's anatomy illustration of orbital gyrus | |||
File:Orbital_gyrus_animation_small2.gif|Animation of orbital gyrus | |||
File:Medial_surface_of_cerebral_cortex_-_gyri.png|Medial surface of cerebral cortex showing gyri | |||
File:Orbital_gyrus_viewed_from_bottom.png|Orbital gyrus viewed from bottom | |||
File:Orbitofrontal_cortex.gif|Orbitofrontal cortex | |||
File:Orbitofrontal_cortex_coronal_sections.gif|Orbitofrontal cortex coronal sections | |||
File:Orbitofrontal_cortex_sagittal_sections.gif|Orbitofrontal cortex sagittal sections | |||
File:Orbitofrontal_cortex_transversal_sections.gif|Orbitofrontal cortex transversal sections | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:24, 18 February 2025
Orbitofrontal cortex
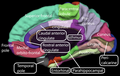
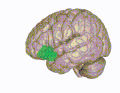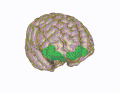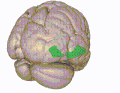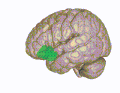
The Orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes in the brain which is involved in the cognitive processing of decision-making. The OFC is considered anatomically synonymous with the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Therefore, the region is distinguished due to the distinct neural connections and the distinct functions it performs. It is defined as the part of the prefrontal cortex that receives projections from the magnocellular, medial nucleus of the mediodorsal thalamus, and is thought to represent emotion in decision making.
Etymology
The term "orbitofrontal cortex" derives from its position immediately above the orbits in which the eyes are located. "Orbito-" is a prefix from Latin "orbita" meaning "course, track" and "-frontal" is derived from Latin "frons" (forehead).
Anatomy
The OFC is divided into the medial and lateral OFC. The medial part is associated with monitoring the value of rewards and the lateral part is associated with evaluating punishments. The OFC contains the secondary olfactory cortex, which receives information about odours from the primary olfactory cortex.
Function
The orbitofrontal cortex plays a key role in decision making and expectation. It is involved in sensory integration, in representing the affective value of reinforcers, and in decision-making and expectation. The OFC is also involved in social and emotional processing, and lesions in this area can lead to deficits in interpreting and responding to social and emotional cues.
Clinical significance
Damage to the OFC can lead to a variety of disorders and abnormalities in cognitive function. These include impulsivity, compulsivity, mood disorders, and drug addiction. Patients with damage to the OFC can also exhibit personality changes and difficulty in making and following through with plans.
See also
References
<references />
|
|
|
-
MRI of orbitofrontal cortex
-
Gray's anatomy illustration of orbital gyrus
-
Animation of orbital gyrus
-
Medial surface of cerebral cortex showing gyri
-
Orbital gyrus viewed from bottom
-
Orbitofrontal cortex
-
Orbitofrontal cortex coronal sections
-
Orbitofrontal cortex sagittal sections
-
Orbitofrontal cortex transversal sections