Common interosseous artery: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
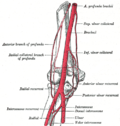
File:Gray526.png|Common interosseous artery | |||
File:Gray529.png|Common interosseous artery | |||
File:Gray528.png|Common interosseous artery | |||
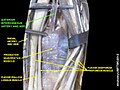
File:Slide3MMMMM.JPG|Common interosseous artery | |||
File:Slide8MMMM.JPG|Common interosseous artery | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:33, 18 February 2025
Common Interosseous Artery
The Common Interosseous Artery (CIA) is a branch of the Ulnar Artery that supplies blood to the forearm and hand. The term "interosseous" is derived from the Latin words "inter" (between) and "osseus" (bony), referring to the artery's location between the bones of the forearm.
Anatomy[edit]
The Common Interosseous Artery typically arises from the ulnar artery near the elbow. It divides into two main branches: the Anterior Interosseous Artery and the Posterior Interosseous Artery. These branches travel down the forearm, between the radius and ulna bones, supplying blood to the muscles and skin of the forearm and hand.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the Common Interosseous Artery is to supply blood to the deep structures of the forearm. It does this through its two main branches, the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. These arteries provide oxygenated blood to the muscles, bones, and skin of the forearm and hand.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The Common Interosseous Artery is an important structure in the field of vascular surgery. It can be involved in various medical conditions, such as Peripheral Artery Disease and Compartment Syndrome. Knowledge of its anatomy is crucial for procedures such as angiography and bypass surgery.
See Also[edit]
- Ulnar Artery
- Anterior Interosseous Artery
- Posterior Interosseous Artery
- Peripheral Artery Disease
- Compartment Syndrome
References[edit]
<references />