Carotid groove: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:Medical terminology]] | [[Category:Medical terminology]] | ||
[[Category:Human skull]] | [[Category:Human skull]] | ||
== Carotid groove == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray145.png | |||
File:Gray193.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:50, 17 February 2025
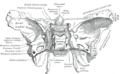
Carotid Groove is a term used in anatomy to describe a specific structure found in the human skull. It is a groove in the petrous part of the temporal bone where the internal carotid artery lies. The term "carotid" is derived from the Greek word "karōtides" which means "drowsiness", as pressure on these arteries was believed to cause a state of unconsciousness.
Anatomy[edit]
The Carotid Groove is located in the petrous part of the temporal bone, which is one of the hardest parts of the skull. The groove is formed by the internal carotid artery as it ascends from the neck to the brain. The artery lies in this groove as it passes through the carotid canal.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the Carotid Groove is to provide a pathway for the internal carotid artery. This artery is one of the major blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. It is therefore crucial for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the brain.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The Carotid Groove can be of clinical significance in cases of trauma or disease. For example, fractures involving the temporal bone could potentially damage the internal carotid artery as it lies in the Carotid Groove. This could lead to serious complications such as stroke or hemorrhage. Furthermore, diseases that cause narrowing or blockage of the internal carotid artery, such as atherosclerosis, could also affect the Carotid Groove.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />