Internodal segment: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | [[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Neurophysiology]] | [[Category:Neurophysiology]] | ||
= Internodal segment = | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray631.png | |||
File:Gray634.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:00, 17 February 2025
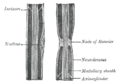
Internodal Segment
The Internodal Segment is a crucial part of the neuron that plays a significant role in the transmission of nerve impulses. It is the part of the axon that is located between two consecutive Nodes of Ranvier.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Internodal Segment" is derived from the Latin words "inter" meaning between, "nodus" meaning knot, and "segmentum" meaning a piece cut off. Thus, it refers to the piece of the axon that is cut off between two knots or nodes.
Structure[edit]
The Internodal Segment is a part of the axon that is covered by the myelin sheath, a fatty insulating layer that speeds up the transmission of nerve impulses. The myelin sheath is interrupted at regular intervals by the Nodes of Ranvier, and the parts of the axon between these nodes are referred to as Internodal Segments.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the Internodal Segment is to facilitate the rapid transmission of nerve impulses along the axon. This is achieved through a process known as saltatory conduction, where the nerve impulse jumps from one Node of Ranvier to the next, skipping over the Internodal Segments. This allows the nerve impulse to travel much faster than it would if it had to travel the entire length of the axon.
Related Terms[edit]
- Axon: The long, threadlike part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells.
- Nodes of Ranvier: Small gaps in the insulating myelin sheath where the axon is exposed.
- Myelin Sheath: A layer of fatty tissue that protects and insulates the axon, increasing the speed at which nerve impulses can travel.
- Saltatory Conduction: The process by which nerve impulses jump from one Node of Ranvier to the next, speeding up their transmission along the axon.