Periodic function: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
[[Category:Physics]] | [[Category:Physics]] | ||
[[Category:Engineering]] | [[Category:Engineering]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Periodic_function_illustration.svg|Illustration of a periodic function | |||
File:Sine.svg|Graph of the sine function | |||
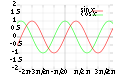
File:Sine_cosine_plot.svg|Plot of sine and cosine functions | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:40, 18 February 2025
Periodic Function[edit]
A periodic function is a mathematical function that repeats its values at regular intervals. These intervals are called periods, and the smallest positive period is known as the fundamental period. Periodic functions are widely used in various fields of mathematics, physics, engineering, and signal processing.
Definition[edit]
A function f(x) is said to be periodic if there exists a positive number T such that f(x + T) = f(x) for all values of x in the domain of the function. The number T is called the period of the function. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
f(x + T) = f(x)
Periodic functions can have different types of periods, such as finite periods, infinite periods, or even non-integer periods. The most common example of a periodic function is the trigonometric function, sine (sin(x)), which repeats itself every 2π radians or 360 degrees.
Properties[edit]
Periodic functions possess several important properties that make them useful in various applications. Some of these properties include:
1. Periodicity: As mentioned earlier, periodic functions repeat their values at regular intervals. This property allows for the analysis and prediction of the behavior of the function over time.
2. Symmetry: Many periodic functions exhibit symmetry about certain points or lines. For example, the sine function is symmetric about the origin, while the cosine function is symmetric about the y-axis.
3. Fourier Series: Periodic functions can be represented as a sum of sine and cosine functions through the Fourier series. This representation allows for the decomposition of complex periodic functions into simpler components, making them easier to analyze.
4. Harmonic Analysis: Periodic functions are extensively used in harmonic analysis, which deals with the study of the composition of periodic functions and their harmonics. This field finds applications in music, signal processing, and electrical engineering.
Examples[edit]
There are numerous examples of periodic functions in mathematics and other disciplines. Some common examples include:
1. Trigonometric Functions: Sine (sin(x)), cosine (cos(x)), and tangent (tan(x)) functions are periodic with a period of 2π radians or 360 degrees.
2. Square Wave: The square wave function is periodic with a period of 2, alternating between two constant values.
3. Sawtooth Wave: The sawtooth wave function is periodic with a period of 2π, continuously increasing or decreasing linearly.
4. Dirac Comb: The Dirac comb function is periodic with an infinite period, consisting of a series of Dirac delta functions spaced at regular intervals.
Applications[edit]
Periodic functions find applications in various fields, including:
1. Physics: Periodic functions are used to describe the behavior of physical phenomena that exhibit periodicity, such as oscillations, waves, and vibrations.
2. Engineering: Periodic functions are used in engineering disciplines, such as electrical engineering, to analyze and design systems that involve periodic signals, such as AC circuits and communication systems.
3. Signal Processing: Periodic functions are fundamental in signal processing, where they are used to analyze and manipulate signals, such as audio, video, and communication signals.
4. Mathematics: Periodic functions play a crucial role in mathematical analysis, differential equations, and the study of harmonic functions.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
1. Bracewell, R. N. (2000). The Fourier Transform and Its Applications. McGraw-Hill Education.
2. Oppenheim, A. V., & Schafer, R. W. (2010). Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Pearson Education.
3. Strang, G. (1993). Introduction to Applied Mathematics. Wellesley-Cambridge Press.
Categories[edit]
-
Illustration of a periodic function
-
Graph of the sine function
-
Plot of sine and cosine functions