Central neurocytoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A rare type of brain tumor}} | {{Short description|A rare type of brain tumor}} | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) | |||
| name = Central neurocytoma | |||
| synonyms = Intraventricular neurocytoma | |||
| image = Neurocytome axiale.jpg | |||
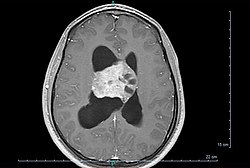
| caption = Axial T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced MRI image showing an enhancing mass with cystic changes consistent with central neurocytoma in the right lateral ventricle. | |||
| pronounce = | |||
| field = [[Oncology]], [[neurosurgery]], [[neuropathology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[visual disturbances]], [[hydrocephalus]], [[seizures]] | |||
| complications = Obstructive [[hydrocephalus]], recurrence, postoperative complications | |||
| onset = Typically in young adults (20–40 years) | |||
| duration = Chronic, may recur | |||
| types = Central and extraventricular neurocytoma | |||
| causes = Unknown; believed to be related to neuronal progenitor cells | |||
| risks = No clear environmental or genetic risk factors identified | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[CT scan]], [[biopsy]], histopathology with immunohistochemical markers (e.g., synaptophysin positive) | |||
| differential = [[Ependymoma]], [[oligodendroglioma]], [[subependymal giant cell astrocytoma]], [[choroid plexus papilloma]] | |||
| prevention = None known | |||
| treatment = Surgical resection (gross total or subtotal), [[radiation therapy]] for residual or recurrent tumors | |||
| medication = Not typically used; symptomatic treatment for increased intracranial pressure | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with complete resection; 5-year survival ~80–90% | |||
| frequency = Rare; accounts for <1% of all brain tumors | |||
| deaths = Rare with proper treatment | |||
}} | |||
'''Central neurocytoma''' is a rare [[brain tumor]] that typically arises in the [[ventricular system]] of the [[central nervous system]]. It is considered a [[neuroepithelial tumor]] and is most commonly found in young adults. | '''Central neurocytoma''' is a rare [[brain tumor]] that typically arises in the [[ventricular system]] of the [[central nervous system]]. It is considered a [[neuroepithelial tumor]] and is most commonly found in young adults. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 40: | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for patients with central neurocytoma is generally favorable, especially when the tumor is completely resected. The recurrence rate is low, and long-term survival is common. However, incomplete resection may lead to recurrence, necessitating further treatment. | The prognosis for patients with central neurocytoma is generally favorable, especially when the tumor is completely resected. The recurrence rate is low, and long-term survival is common. However, incomplete resection may lead to recurrence, necessitating further treatment. | ||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: Central neurocytoma - 2 - high mag.jpg | High mag. | |||
Image: Central neurocytoma - 2 - very high mag.jpg | Very high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Related pages== | ==Related pages== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 52: | ||
* [[Oligodendroglioma]] | * [[Oligodendroglioma]] | ||
== External links == | |||
{{Medical resources | |||
| DiseasesDB = | |||
| ICD10 = | |||
| ICD9 = | |||
| OMIM = | |||
| MedlinePlus = | |||
| ICDO = ICD-O 9506/1 | |||
| eMedicineSubj = med | |||
| eMedicineTopic = 1346305 | |||
| MeshID = D018306 | |||
}} | |||
{{Commons category|Central neurocytoma}} | |||
{{Central nervous system tumors}} | |||
{{stub}} | |||
[[Category:Brain tumors]] | [[Category:Brain tumors]] | ||
[[Category:Neuroepithelial tumors]] | [[Category:Neuroepithelial tumors]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:40, 26 March 2025
A rare type of brain tumor
| Central neurocytoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Intraventricular neurocytoma |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Oncology, neurosurgery, neuropathology |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances, hydrocephalus, seizures |
| Complications | Obstructive hydrocephalus, recurrence, postoperative complications |
| Onset | Typically in young adults (20–40 years) |
| Duration | Chronic, may recur |
| Types | Central and extraventricular neurocytoma |
| Causes | Unknown; believed to be related to neuronal progenitor cells |
| Risks | No clear environmental or genetic risk factors identified |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, biopsy, histopathology with immunohistochemical markers (e.g., synaptophysin positive) |
| Differential diagnosis | Ependymoma, oligodendroglioma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, choroid plexus papilloma |
| Prevention | None known |
| Treatment | Surgical resection (gross total or subtotal), radiation therapy for residual or recurrent tumors |
| Medication | Not typically used; symptomatic treatment for increased intracranial pressure |
| Prognosis | Generally good with complete resection; 5-year survival ~80–90% |
| Frequency | Rare; accounts for <1% of all brain tumors |
| Deaths | Rare with proper treatment |
Central neurocytoma is a rare brain tumor that typically arises in the ventricular system of the central nervous system. It is considered a neuroepithelial tumor and is most commonly found in young adults.
Presentation[edit]
Central neurocytomas are usually located in the lateral ventricles near the foramen of Monro. Patients often present with symptoms related to increased intracranial pressure, such as headache, nausea, and vomiting. Other symptoms may include vision problems, seizures, and cognitive changes.
Pathology[edit]
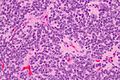
Central neurocytomas are classified as WHO Grade II tumors, indicating a low-grade malignancy. Histologically, they are composed of small, round cells with uniform nuclei and a moderate amount of cytoplasm. The tumor cells often form clusters and rosettes, resembling oligodendrogliomas. The presence of synaptophysin positivity on immunohistochemistry is a characteristic feature.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of central neurocytoma is typically made through a combination of neuroimaging and histopathological examination. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred imaging modality, often revealing a well-circumscribed mass in the ventricular system. Computed tomography (CT) scans may show calcifications within the tumor.
Treatment[edit]
The primary treatment for central neurocytoma is surgical resection. Complete removal of the tumor is often curative, but in cases where total resection is not possible, radiotherapy may be considered. The role of chemotherapy is limited and not well established.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with central neurocytoma is generally favorable, especially when the tumor is completely resected. The recurrence rate is low, and long-term survival is common. However, incomplete resection may lead to recurrence, necessitating further treatment.
Gallery[edit]
-
High mag.
-
Very high mag.
Related pages[edit]
External links[edit]
| Tumours of the nervous system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Note: Not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see brain metastasis).
|