Dihydroergocornine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Category:Chemical Compounds]] | [[Category:Chemical Compounds]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Dihydroergocornine.svg|Dihydroergocornine | File:Dihydroergocornine.svg|Dihydroergocornine | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:27, 16 March 2025
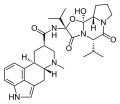
Dihydroergocornine
Dihydroergocornine is a chemical compound that belongs to the ergoline family of alkaloids. It is a derivative of ergocornine and is closely related to other ergot alkaloids such as ergotamine and ergonovine. Dihydroergocornine is primarily found in certain species of fungi, particularly in the genus Claviceps, which are known to infect various grains such as rye.
Chemical Structure: Dihydroergocornine has a complex chemical structure consisting of a tetracyclic ergoline ring system. It is a semi-synthetic compound derived from ergocornine through hydrogenation of the double bond in the ergoline ring. The chemical formula of dihydroergocornine is C20H25N3O.
Biological Activity: Dihydroergocornine exhibits pharmacological properties similar to other ergot alkaloids. It acts as a partial agonist at various serotonin and dopamine receptors in the central nervous system. It also has vasoconstrictive effects due to its action on alpha-adrenergic receptors. Dihydroergocornine is used in the treatment of certain medical conditions, including migraines and postpartum hemorrhage.
Clinical Applications: In clinical practice, dihydroergocornine is sometimes used as a component of combination medications for the management of migraines. It is believed to help alleviate migraine symptoms by constricting blood vessels in the brain. Additionally, dihydroergocornine has been investigated for its potential role in preventing postpartum hemorrhage by promoting uterine contractions.
Side Effects: Like other ergot alkaloids, dihydroergocornine can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and peripheral vasoconstriction. In high doses, it may lead to more severe adverse reactions, including hallucinations and ischemic events. Patients should be monitored closely when using medications containing dihydroergocornine to minimize the risk of complications.
Research and Development: Research is ongoing to explore the full therapeutic potential of dihydroergocornine and its derivatives. Scientists are investigating its effects on various receptors and signaling pathways to better understand its mechanism of action. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop novel formulations of dihydroergocornine with improved efficacy and safety profiles.
-
Dihydroergocornine