Inner ear: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Blausen_0329_EarAnatomy_InternalEar.png|Inner ear|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Gray920.png|Inner ear|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Gray923.png|Inner ear|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Cochlea-crosssection.svg|Inner ear|thumb]] | |||
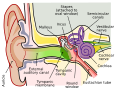
'''Inner ear''' is the innermost part of the [[ear]], a complex structure responsible for [[sound]] detection and balance. It is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear houses the [[vestibular system]], which contributes to our sense of balance and spatial orientation, and the [[cochlea]], which detects sound. | '''Inner ear''' is the innermost part of the [[ear]], a complex structure responsible for [[sound]] detection and balance. It is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear houses the [[vestibular system]], which contributes to our sense of balance and spatial orientation, and the [[cochlea]], which detects sound. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 24: | ||
There are several disorders that can affect the inner ear, including [[Meniere's disease]], [[vestibular neuritis]], and [[labyrinthitis]]. These conditions can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, tinnitus, and hearing loss. | There are several disorders that can affect the inner ear, including [[Meniere's disease]], [[vestibular neuritis]], and [[labyrinthitis]]. These conditions can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, tinnitus, and hearing loss. | ||
== Additional images == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Organ_of_corti.svg|Inner ear | |||
File:Anatomy_of_the_Human_Ear.svg|Inner ear | |||
File:Ear_labyrinth.jpg|Inner ear | |||
File:Oreille_Interne.png|Inner ear | |||
File:Temporal_bone2.jpg|Inner ear | |||
File:Gray925.png|Inner ear | |||
File:1408_Frequency_Coding_in_The_Cochlea.jpg|Inner ear | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Ear]] | * [[Ear]] | ||
* [[Hearing]] | * [[Hearing]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 43: | ||
* [[Vestibular neuritis]] | * [[Vestibular neuritis]] | ||
* [[Labyrinthitis]] | * [[Labyrinthitis]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Ear]] | [[Category:Ear]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 49: | ||
[[Category:Balance]] | [[Category:Balance]] | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:58, 28 April 2025
Inner ear is the innermost part of the ear, a complex structure responsible for sound detection and balance. It is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear houses the vestibular system, which contributes to our sense of balance and spatial orientation, and the cochlea, which detects sound.
Anatomy[edit]
The inner ear is composed of two main parts: the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is a system of passages making up two main functional parts: the cochlea and the vestibular system. The cochlea is involved in hearing, while the vestibular system helps with balance.
Cochlea[edit]
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, making it the main organ of hearing. It is divided into three fluid-filled spaces: the scala vestibuli, the scala media, and the scala tympani. The organ of Corti, located within the scala media, is the sensory receptor organ for hearing.
Vestibular system[edit]
The vestibular system is the region of the inner ear where the semicircular canals converge, close to the cochlea. The vestibular system is responsible for providing our brain with information about our body's motion and orientation in space.
Function[edit]
The inner ear performs two major functions: hearing and balance. The cochlea converts sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electro-chemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. The vestibular system is responsible for maintaining our body's balance.
Disorders[edit]
There are several disorders that can affect the inner ear, including Meniere's disease, vestibular neuritis, and labyrinthitis. These conditions can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, tinnitus, and hearing loss.
Additional images[edit]
-
Inner ear
-
Inner ear
-
Inner ear
-
Inner ear
-
Inner ear
-
Inner ear
-
Inner ear