Brodmann area 12: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Brodmann area 12, a region of the cerebral cortex}} | |||
== | [[File:Brodmann_area_12_animation_small.gif|Brodmann area 12 animation|thumb|right]] | ||
Brodmann area 12 is located in the [[frontal lobe]] | |||
'''Brodmann area 12''' is a subdivision of the [[cerebral cortex]] in the brain, defined based on its [[cytoarchitecture]]. It is part of the [[frontal lobe]] and is involved in various higher cognitive functions. This area is named after [[Korbinian Brodmann]], who first described it in the early 20th century. | |||
==Anatomy== | |||
[[File:Brodmann_area_12_frontal.jpg|Brodmann area 12 frontal view|thumb|left]] | |||
Brodmann area 12 is located in the [[frontal lobe]] of the [[cerebral cortex]]. It is situated anterior to [[Brodmann area 11]] and is often considered part of the [[orbitofrontal cortex]]. The precise boundaries of Brodmann area 12 can vary between individuals, but it is generally found on the ventral surface of the frontal lobe. | |||
==Cytoarchitecture== | |||
[[File:Brodmann_Cytoarchitectonics_12.png|Brodmann area 12 cytoarchitectonics|thumb|right]] | |||
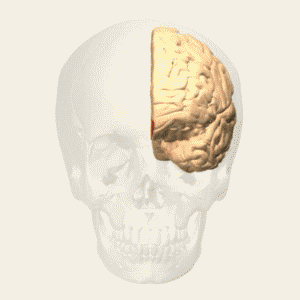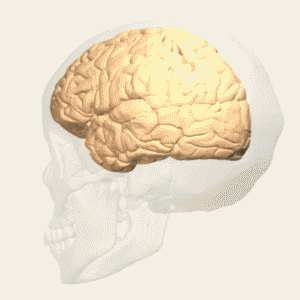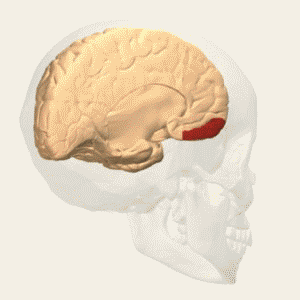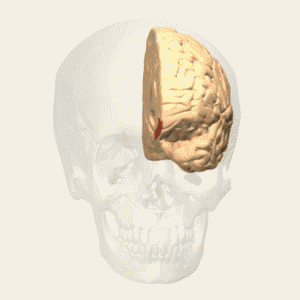
The cytoarchitecture of Brodmann area 12 is characterized by a distinct layering of neurons. This area is known for its granular appearance, with a prominent layer IV, which is typical of sensory areas. The organization of neurons in Brodmann area 12 suggests its involvement in complex processing tasks. | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
Brodmann area 12 is associated with a variety of cognitive functions, including decision making, social behavior, and emotional regulation. It is part of the [[prefrontal cortex]], which is crucial for executive functions such as planning, reasoning, and problem-solving. The orbitofrontal location of Brodmann area 12 suggests its involvement in processing reward-related information and evaluating the emotional significance of stimuli. | |||
==Clinical | ==Clinical significance== | ||
Dysfunction in Brodmann area 12 has been implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders. Abnormalities in this region may contribute to conditions such as [[obsessive-compulsive disorder]], [[depression]], and [[schizophrenia]]. Understanding the role of Brodmann area 12 in these disorders is an ongoing area of research. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Brodmann area 11]] | |||
* [[Orbitofrontal cortex]] | |||
* [[Prefrontal cortex]] | |||
* [[Korbinian Brodmann]] | |||
==See | [[File:Brodmann_area_12_medial.jpg|Brodmann area 12 medial view|thumb|left]] | ||
* [[Brodmann | |||
* [[ | ==See also== | ||
* [[List of Brodmann areas]] | |||
* [[Cerebral cortex]] | |||
* [[Frontal lobe]] | * [[Frontal lobe]] | ||
[[Category: | {{Brodmann areas}} | ||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Brodmann areas]] | ||
[[Category:Frontal lobe]] | |||
[[Category:Cerebral cortex]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:47, 23 March 2025
Brodmann area 12, a region of the cerebral cortex
Brodmann area 12 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex in the brain, defined based on its cytoarchitecture. It is part of the frontal lobe and is involved in various higher cognitive functions. This area is named after Korbinian Brodmann, who first described it in the early 20th century.
Anatomy[edit]

Brodmann area 12 is located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is situated anterior to Brodmann area 11 and is often considered part of the orbitofrontal cortex. The precise boundaries of Brodmann area 12 can vary between individuals, but it is generally found on the ventral surface of the frontal lobe.
Cytoarchitecture[edit]

The cytoarchitecture of Brodmann area 12 is characterized by a distinct layering of neurons. This area is known for its granular appearance, with a prominent layer IV, which is typical of sensory areas. The organization of neurons in Brodmann area 12 suggests its involvement in complex processing tasks.
Function[edit]
Brodmann area 12 is associated with a variety of cognitive functions, including decision making, social behavior, and emotional regulation. It is part of the prefrontal cortex, which is crucial for executive functions such as planning, reasoning, and problem-solving. The orbitofrontal location of Brodmann area 12 suggests its involvement in processing reward-related information and evaluating the emotional significance of stimuli.
Clinical significance[edit]
Dysfunction in Brodmann area 12 has been implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders. Abnormalities in this region may contribute to conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, and schizophrenia. Understanding the role of Brodmann area 12 in these disorders is an ongoing area of research.
Related pages[edit]
