Somatostatin receptor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Somatostatin Receptor == | == Somatostatin Receptor == | ||
Somatostatin receptors are a group of [[G protein-coupled receptors]] (GPCRs) that bind the peptide hormone [[somatostatin]]. These receptors are involved in a wide range of biological processes, including the inhibition of hormone secretion, modulation of neurotransmission, and regulation of cell proliferation. | Somatostatin receptors are a group of [[G protein-coupled receptors]] (GPCRs) that bind the peptide hormone [[somatostatin]]. These receptors are involved in a wide range of biological processes, including the inhibition of hormone secretion, modulation of neurotransmission, and regulation of cell proliferation. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Receptors]] | [[Category:Receptors]] | ||
[[Category:Endocrinology]] | [[Category:Endocrinology]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:⁹⁰Y-DOTATOC_Structure.jpg|⁹⁰Y-DOTATOC Structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:03, 23 February 2025
Somatostatin Receptor[edit]
Somatostatin receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that bind the peptide hormone somatostatin. These receptors are involved in a wide range of biological processes, including the inhibition of hormone secretion, modulation of neurotransmission, and regulation of cell proliferation.
Types of Somatostatin Receptors[edit]
There are five known subtypes of somatostatin receptors, designated as SSTR1, SSTR2, SSTR3, SSTR4, and SSTR5. Each subtype has distinct tissue distribution and functional roles:
- SSTR1: Predominantly found in the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
- SSTR2: Widely expressed in the pituitary gland, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract.
- SSTR3: Present in the brain, pancreas, and kidney.
- SSTR4: Mainly located in the lung and brain.
- SSTR5: Found in the pituitary gland and pancreas.
Function[edit]
Somatostatin receptors mediate the effects of somatostatin by inhibiting the release of various secondary hormones. For example, in the pituitary gland, somatostatin inhibits the secretion of growth hormone. In the pancreas, it suppresses the release of insulin and glucagon.
Clinical Significance[edit]
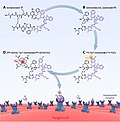
Somatostatin receptors are targets for diagnostic and therapeutic applications, particularly in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors. Radiolabeled somatostatin analogs, such as __Y-DOTATOC, are used in peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) to deliver targeted radiation to tumor cells expressing somatostatin receptors.
Related Pages[edit]
-
⁹⁰Y-DOTATOC Structure