Ajoene: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
[[Category:Antimicrobials]] | [[Category:Antimicrobials]] | ||
[[Category:Antithrombotic agents]] | [[Category:Antithrombotic agents]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ajoene.svg|Ajoene chemical structure | |||
File:(S,E)-ajoene-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png|(S,E)-Ajoene 3D structure | |||
File:Mechanism_for_formation_of_ajoene_from_allicin.tiff|Mechanism for formation of ajoene from allicin | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 03:48, 18 February 2025
A sulfur-containing compound derived from garlic
Ajoene is a sulfur-containing compound derived from garlic (Allium sativum). It is known for its potential medicinal properties, including antimicrobial, antithrombotic, and anticancer effects. Ajoene is formed from allicin, another compound found in garlic, through a series of chemical reactions.
Chemical Structure[edit]
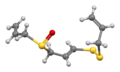
Ajoene is a compound that contains sulfur atoms and is characterized by its unique structure. It exists in two isomeric forms, E-ajoene and Z-ajoene, which differ in the configuration around the double bond. The chemical structure of ajoene is represented by the following image:

Formation[edit]
Ajoene is formed from allicin, which is produced when garlic is crushed or chopped. The enzyme alliinase converts alliin into allicin, which then undergoes further transformation to form ajoene. The mechanism of formation involves the rearrangement of allicin molecules, as shown in the following diagram:
Biological Activity[edit]
Ajoene exhibits a range of biological activities that contribute to its potential therapeutic effects.
Antimicrobial Properties[edit]
Ajoene has been shown to possess antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a variety of bacteria, fungi, and viruses. It disrupts microbial cell membranes and inhibits the growth of pathogens.
Antithrombotic Effects[edit]
Ajoene has antithrombotic properties, meaning it can prevent the formation of blood clots. It inhibits platelet aggregation, which is a crucial step in the clotting process, thereby reducing the risk of thrombosis.
Anticancer Potential[edit]
Research suggests that ajoene may have anticancer properties. It can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth. Ajoene's ability to modulate signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation makes it a compound of interest in cancer research.
Applications[edit]
Due to its biological activities, ajoene is being studied for various applications in medicine and health.
Pharmaceuticals[edit]
Ajoene is being explored as a potential ingredient in pharmaceutical formulations aimed at treating infections, preventing thrombosis, and combating cancer.
Nutraceuticals[edit]
As a natural compound derived from garlic, ajoene is also considered for use in nutraceuticals, which are products derived from food sources with extra health benefits.
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
3D structure of ajoene
-
Ajoene chemical structure
-
(S,E)-Ajoene 3D structure
-
Mechanism for formation of ajoene from allicin