Transplantable organs and tissues: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
[[Category:Transplantation medicine]] | [[Category:Transplantation medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Medical procedures]] | [[Category:Medical procedures]] | ||
<gallery caption="Transplantable_organs_and_tissues"> | |||
File:Heart_transplant.jpg|Heart transplant | |||
File:kidtransplant.svg|Kidney transplant | |||
File:Cornea_transplant800.jpg|Cornea transplant | |||
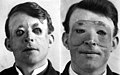
File:Walter_Yeo_skin_graft.jpg|Skin graft on Walter Yeo | |||
File:Fra_Angelico_064.jpg|Transplantable organs and tissues | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:55, 18 February 2025
Transplantable Organs and Tissues[edit]

Transplantable organs and tissues are those that can be transferred from one body to another to replace damaged or absent organs or tissues. The process of transplantation involves the removal of the organ or tissue from a donor and its implantation into a recipient. This medical procedure is critical for patients with organ failure or severe tissue damage.
Types of Transplantable Organs[edit]
Heart[edit]

The heart is a vital organ that can be transplanted in patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease. Heart transplants are complex procedures that require careful matching of donor and recipient.
Kidneys[edit]

The kidney is one of the most commonly transplanted organs. Kidney transplants are performed on patients with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal failure. Living or deceased donors can provide kidneys for transplantation.
Liver[edit]
The liver is another organ that can be transplanted. Liver transplants are necessary for patients with liver failure due to conditions such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.
Lungs[edit]
Lung transplants are performed for patients with severe respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cystic fibrosis.
Pancreas[edit]
The pancreas can be transplanted to treat patients with type 1 diabetes, often in conjunction with a kidney transplant.
Intestines[edit]
Intestinal transplants are less common but can be performed for patients with short bowel syndrome or other severe intestinal diseases.
Types of Transplantable Tissues[edit]
Cornea[edit]

The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye. Corneal transplants can restore vision in patients with corneal damage or disease.
Skin[edit]

Skin grafts are used to treat burn victims or patients with extensive skin loss. Skin can be harvested from donors or grown in laboratories.
Bone Marrow[edit]
Bone marrow transplants are used to treat patients with blood disorders such as leukemia or lymphoma. The procedure involves transplanting healthy bone marrow stem cells to replace damaged or diseased marrow.
Heart Valves[edit]
Heart valve transplants can replace damaged valves in patients with valvular heart disease. Donor valves can be human or animal-derived.
Tendons and Ligaments[edit]
Tendon and ligament transplants are used in orthopedic surgeries to repair damaged joints or tissues.
Ethical and Medical Considerations[edit]
Transplantation raises several ethical and medical issues, including the allocation of scarce organs, the risk of rejection, and the need for lifelong immunosuppression. Advances in medical technology and immunology continue to improve outcomes for transplant recipients.
Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
- Transplantable_organs_and_tissues
-
Heart transplant
-
Kidney transplant
-
Cornea transplant
-
Skin graft on Walter Yeo
-
Transplantable organs and tissues