Umbellulone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
[[Category:Ketones]] | [[Category:Ketones]] | ||
[[Category:Natural products]] | [[Category:Natural products]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Structuurformule_umbellulone.png|Structuurformule van Umbellulone | |||
File:Structuurfomules_umbellulone.png|Structuurformules van Umbellulone | |||
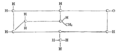
File:Reactie_mechanisme.png|Reactiemechanisme van Umbellulone | |||
File:MEchanismebio.png|Biologisch mechanisme van Umbellulone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:01, 18 February 2025
Chemical compound
| Chemical Compound | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molar Mass | |
| Appearance | |
| Density | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Pictograms | [[File:|50px]] |
| GHS Signal Word | |
| GHS Hazard Statements | |
| NFPA 704 | [[File:|50px]] |
| References | |
Umbellulone is a naturally occurring organic compound found in the leaves of the California bay laurel (Umbellularia californica), a tree native to the coastal forests of California and Oregon. It is a monoterpene ketone and is known for its distinctive aroma and potential biological effects.
Chemical structure and properties[edit]
Umbellulone is classified as a monoterpene ketone. Its chemical formula is C10H14O, and it has a molecular weight of 150.22 g/mol. The compound is characterized by a bicyclic structure, which includes a cyclohexene ring fused to a cyclopropane ring. This unique structure contributes to its reactivity and biological activity.
Occurrence[edit]
Umbellulone is primarily found in the leaves of the California bay laurel. The leaves of this tree are known for their strong, pungent aroma, which is largely attributed to the presence of umbellulone and other volatile compounds. The tree is commonly found in the coastal regions of California and Oregon, where it grows in mixed evergreen forests.
Biological effects[edit]
Umbellulone has been studied for its potential biological effects, particularly its impact on the trigeminal nerve. It is known to be a potent irritant and can induce headaches in sensitive individuals. This effect is thought to be due to its ability to activate the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing.
Mechanism of action[edit]
The mechanism by which umbellulone exerts its effects involves the activation of the TRPA1 ion channel, a receptor known to mediate pain and inflammation. Upon inhalation, umbellulone can bind to and activate TRPA1, leading to the release of neuropeptides and the sensation of pain or discomfort.
Safety and toxicity[edit]
While umbellulone is a natural compound, it can be toxic in high concentrations. Exposure to the vapors of umbellulone can cause irritation of the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Individuals handling the compound or working with California bay laurel leaves should take precautions to avoid excessive exposure.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Structuurformule van Umbellulone
-
Structuurformules van Umbellulone
-
Reactiemechanisme van Umbellulone
-
Biologisch mechanisme van Umbellulone