Global digital divide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Global_digital_divide == | |||
<gallery> | |||
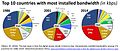
File:GlobalBandwidthConcentration.jpg|Global Bandwidth Concentration | |||
File:InternetPenetrationWorldMap.svg|Internet Penetration World Map | |||
File:Internet_users_per_100_inhabitants_ITU.svg|Internet Users per 100 Inhabitants | |||
File:MobileBroadbandInternetPenetrationWorldMap_2013.svg|Mobile Broadband Internet Penetration World Map 2013 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:35, 18 February 2025
Global Digital Divide refers to the gap between individuals, households, businesses, and geographic areas at different socio-economic levels with regard to their opportunities to access information and communication technologies (ICTs). The divide not only encompasses the access to the internet and computer technology but also the ability to use the technology effectively. The global digital divide primarily highlights the divide between the developed countries and the developing countries, often referred to as the North-South divide.
Causes[edit]
The causes of the global digital divide are multifaceted and include economic, social, and political factors. Key factors include:
- Economic Barriers: The cost of technology and internet access remains prohibitively high for many people in developing countries.
- Infrastructure: Many developing countries lack the necessary infrastructure for internet access and high-speed connectivity.
- Education and Skills: A lack of education and digital literacy skills prevents individuals from effectively using ICTs.
- Language: Much of the content available on the internet is in English, which can be a barrier for non-English speakers.
- Government Policies: In some countries, government policies may restrict access to the internet or fail to prioritize ICT development.
Impact[edit]
The global digital divide has significant implications for education, economic development, and social inclusion. It affects individuals' ability to access educational resources, participate in the digital economy, and engage with digital government services. The divide also impacts the ability of countries to compete in the global market, innovate, and achieve sustainable development goals.
Bridging the Divide[edit]
Efforts to bridge the global digital divide include international cooperation, national policies, and initiatives by non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and the private sector. Strategies include:
- Developing affordable and sustainable ICT infrastructure.
- Promoting digital literacy and education.
- Creating content in multiple languages.
- Implementing policies that ensure equitable access to technology.