Argininosuccinate synthase: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Argininosuccinate | == Argininosuccinate Synthase == | ||
[[File:Human_Argininosuccinate_Synthetase_tetramer_PDB_2NZ2.png|thumb|right|Human Argininosuccinate Synthetase tetramer]] | |||
'''Argininosuccinate synthase''' is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the [[urea cycle]], which is essential for the detoxification of ammonia in the liver. This enzyme catalyzes the condensation of [[citrulline]] and [[aspartate]] to form [[argininosuccinate]], a key step in the conversion of ammonia to urea. | |||
== Structure == | |||
Argininosuccinate synthase is a homotetramer, meaning it is composed of four identical subunits. Each subunit contributes to the formation of the active site where the catalytic reaction occurs. The enzyme is encoded by the ASS1 gene in humans. | |||
[[File:Active_site_of_Thermus_thermophilus_argininosuccinate_synthetase_01.png|thumb|left|Active site of Thermus thermophilus argininosuccinate synthetase]] | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The primary function of argininosuccinate synthase is to catalyze the reaction between citrulline and aspartate, producing argininosuccinate. This reaction is ATP-dependent and is a critical step in the urea cycle, which converts toxic ammonia into urea for excretion from the body. | |||
The | |||
== Mechanism == | |||
The enzyme binds ATP and citrulline to form a citrullyl-AMP intermediate. Aspartate then attacks this intermediate, resulting in the formation of argininosuccinate and the release of AMP. This reaction is crucial for the continuation of the urea cycle. | |||
== Clinical Significance == | == Clinical Significance == | ||
== | Deficiencies in argininosuccinate synthase can lead to a disorder known as [[citrullinemia]], which is characterized by elevated levels of citrulline in the blood. This condition can result in severe neurological impairment if not treated promptly. Management typically involves dietary restrictions and supplementation with arginine. | ||
== Related Enzymes == | |||
Argininosuccinate synthase works in conjunction with other enzymes in the urea cycle, including [[ornithine transcarbamylase]], [[argininosuccinate lyase]], and [[arginase]]. These enzymes collectively facilitate the conversion of ammonia to urea. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Urea cycle]] | |||
* [[Citrullinemia]] | |||
* [[Ornithine transcarbamylase]] | |||
* [[Argininosuccinate lyase]] | |||
* [[Arginase]] | |||
[[File:Citrulline_metabolism.png|thumb|right|Citrulline metabolism]] | |||
== External Links == | |||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/445 ASS1 gene - NCBI] | |||
* [https://www.omim.org/entry/107950 OMIM Entry on Argininosuccinate Synthase] | |||
{{Enzymes}} | |||
{{Urea cycle}} | |||
[[Category:Enzymes]] | [[Category:Enzymes]] | ||
[[Category:Urea cycle]] | |||
[[Category:Metabolism]] | [[Category:Metabolism]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:00, 23 March 2025
Argininosuccinate Synthase[edit]

Argininosuccinate synthase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the urea cycle, which is essential for the detoxification of ammonia in the liver. This enzyme catalyzes the condensation of citrulline and aspartate to form argininosuccinate, a key step in the conversion of ammonia to urea.
Structure[edit]
Argininosuccinate synthase is a homotetramer, meaning it is composed of four identical subunits. Each subunit contributes to the formation of the active site where the catalytic reaction occurs. The enzyme is encoded by the ASS1 gene in humans.
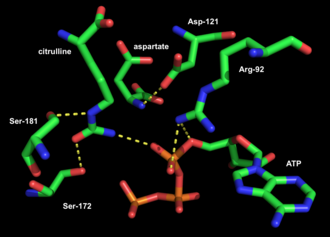
Function[edit]
The primary function of argininosuccinate synthase is to catalyze the reaction between citrulline and aspartate, producing argininosuccinate. This reaction is ATP-dependent and is a critical step in the urea cycle, which converts toxic ammonia into urea for excretion from the body.
Mechanism[edit]
The enzyme binds ATP and citrulline to form a citrullyl-AMP intermediate. Aspartate then attacks this intermediate, resulting in the formation of argininosuccinate and the release of AMP. This reaction is crucial for the continuation of the urea cycle.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Deficiencies in argininosuccinate synthase can lead to a disorder known as citrullinemia, which is characterized by elevated levels of citrulline in the blood. This condition can result in severe neurological impairment if not treated promptly. Management typically involves dietary restrictions and supplementation with arginine.
Related Enzymes[edit]
Argininosuccinate synthase works in conjunction with other enzymes in the urea cycle, including ornithine transcarbamylase, argininosuccinate lyase, and arginase. These enzymes collectively facilitate the conversion of ammonia to urea.
Related Pages[edit]

External Links[edit]
| Enzymes | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|