Vacuum insulated evaporator: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Vacuum Insulated Evaporator == | |||
A ''' | |||
A '''vacuum insulated evaporator''' (VIE) is a device used in industrial applications to store and vaporize cryogenic liquids such as liquid oxygen, nitrogen, or argon. These evaporators are essential in processes where gases are required in large quantities and at specific temperatures and pressures. | |||
A | |||
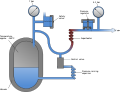
[[File:Vacuum_Insulated_Evaporator_diagram.svg|thumb|Diagram of a Vacuum Insulated Evaporator]] | |||
The | |||
==Applications== | == Design and Function == | ||
Vacuum | |||
The primary function of a vacuum insulated evaporator is to convert cryogenic liquids into gases. This is achieved by utilizing the heat from the surrounding environment to vaporize the liquid stored within the insulated tank. The insulation minimizes heat loss, ensuring efficient vaporization. | |||
A typical VIE consists of a double-walled tank, where the space between the walls is evacuated to create a vacuum. This vacuum acts as an insulator, significantly reducing heat transfer from the outside environment to the cryogenic liquid inside. The inner vessel is usually made of stainless steel to withstand the low temperatures and pressures involved. | |||
== Applications == | |||
==Advantages== | |||
The use of | Vacuum insulated evaporators are widely used in industries such as healthcare, metallurgy, and food processing. In healthcare, they provide a reliable source of medical gases like oxygen and nitrogen. In metallurgy, they are used to supply gases for processes such as welding and cutting. The food industry uses VIEs to preserve and transport perishable goods by maintaining low temperatures. | ||
* | |||
* | == Advantages == | ||
* | The use of vacuum insulation in these evaporators offers several advantages: | ||
== | |||
* '''Efficiency''': The vacuum insulation reduces heat ingress, minimizing the energy required for vaporization. | |||
* '''Safety''': The robust design and materials used ensure safe storage and handling of cryogenic liquids. | |||
* '''Cost-effectiveness''': By reducing heat loss, VIEs lower operational costs associated with maintaining cryogenic temperatures. | |||
== Maintenance and Safety == | |||
[[ | Regular maintenance of vacuum insulated evaporators is crucial to ensure their efficient and safe operation. This includes checking for leaks, inspecting the vacuum integrity, and ensuring that all safety valves and pressure relief devices are functioning correctly. | ||
Safety measures include proper training for personnel handling cryogenic liquids and ensuring that all equipment is compliant with industry standards and regulations. | |||
[[File:Vacuum_Insulated_Evaporator_photo.JPG|thumb|A Vacuum Insulated Evaporator in an industrial setting]] | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Cryogenics]] | |||
* [[Liquid oxygen]] | |||
* [[Liquid nitrogen]] | |||
* [[Industrial gas]] | |||
{{Cryogenics}} | |||
[[Category:Cryogenics]] | [[Category:Cryogenics]] | ||
[[Category:Industrial gases]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Vacuum_Insulated_Evaporator_diagram.svg|Diagram of a Vacuum Insulated Evaporator | |||
File:Vacuum_Insulated_Evaporator_photo.JPG|Photo of a Vacuum Insulated Evaporator | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:57, 18 February 2025
Vacuum Insulated Evaporator[edit]
A vacuum insulated evaporator (VIE) is a device used in industrial applications to store and vaporize cryogenic liquids such as liquid oxygen, nitrogen, or argon. These evaporators are essential in processes where gases are required in large quantities and at specific temperatures and pressures.

Design and Function[edit]
The primary function of a vacuum insulated evaporator is to convert cryogenic liquids into gases. This is achieved by utilizing the heat from the surrounding environment to vaporize the liquid stored within the insulated tank. The insulation minimizes heat loss, ensuring efficient vaporization.
A typical VIE consists of a double-walled tank, where the space between the walls is evacuated to create a vacuum. This vacuum acts as an insulator, significantly reducing heat transfer from the outside environment to the cryogenic liquid inside. The inner vessel is usually made of stainless steel to withstand the low temperatures and pressures involved.
Applications[edit]
Vacuum insulated evaporators are widely used in industries such as healthcare, metallurgy, and food processing. In healthcare, they provide a reliable source of medical gases like oxygen and nitrogen. In metallurgy, they are used to supply gases for processes such as welding and cutting. The food industry uses VIEs to preserve and transport perishable goods by maintaining low temperatures.
Advantages[edit]
The use of vacuum insulation in these evaporators offers several advantages:
- Efficiency: The vacuum insulation reduces heat ingress, minimizing the energy required for vaporization.
- Safety: The robust design and materials used ensure safe storage and handling of cryogenic liquids.
- Cost-effectiveness: By reducing heat loss, VIEs lower operational costs associated with maintaining cryogenic temperatures.
Maintenance and Safety[edit]
Regular maintenance of vacuum insulated evaporators is crucial to ensure their efficient and safe operation. This includes checking for leaks, inspecting the vacuum integrity, and ensuring that all safety valves and pressure relief devices are functioning correctly.
Safety measures include proper training for personnel handling cryogenic liquids and ensuring that all equipment is compliant with industry standards and regulations.

Related Pages[edit]
-
Diagram of a Vacuum Insulated Evaporator
-
Photo of a Vacuum Insulated Evaporator