Typhlosole: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[Category:Invertebrate anatomy]] | [[Category:Invertebrate anatomy]] | ||
{{anatomy-stub}} | {{anatomy-stub}} | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
== Typhlosole == | |||
<gallery> | |||
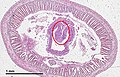
File:Tiflossole_de_oligochaeta.jpg|Tiflossole de oligochaeta | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:08, 17 March 2025
Typhlosole is an anatomical feature found in the digestive systems of certain invertebrates, including many annelids such as earthworms. It is an internal fold of the intestine that extends along its length. The primary function of the typhlosole is to increase the surface area of the intestine, thereby enhancing the absorption of nutrients. This is particularly important in organisms like earthworms, where digestion and absorption need to be highly efficient to meet energy requirements.
Structure and Function[edit]
The typhlosole is characterized by its longitudinal fold that projects into the lumen of the intestine. This fold can vary in complexity and size among different species. In earthworms, the typhlosole is a significant feature of the digestive tract, running almost the entire length of the intestine. It is made up of a mass of cells that serve to increase the surface area available for absorption. By doing so, the typhlosole plays a crucial role in the digestive system, allowing for a more efficient process of nutrient uptake.
In addition to increasing surface area, the typhlosole may also be involved in the secretion of digestive enzymes, further aiding in the breakdown of food particles. The enhanced absorptive and digestive capabilities provided by the typhlosole are vital for the survival of these organisms, enabling them to extract a maximum amount of nutrients from their food.
Comparative Anatomy[edit]
While the typhlosole is a characteristic feature of many annelids, similar structures can be found in other invertebrates, albeit under different names or with slight variations in structure and function. The presence and complexity of such structures often reflect the dietary habits and ecological niches of the organisms. Comparative anatomy studies of the typhlosole and similar structures can provide insights into the evolutionary adaptations of the digestive systems in invertebrates.
Ecological and Biological Significance[edit]
The efficiency of the digestive system in organisms like earthworms, facilitated by structures such as the typhlosole, has significant ecological implications. Earthworms are known for their role in soil aeration and nutrient cycling, processes that are intimately linked to their digestive activities. The enhanced nutrient absorption enabled by the typhlosole allows earthworms to thrive in a variety of soil types, contributing to their ecological success and their ability to improve soil health and fertility.
Conclusion[edit]
The typhlosole is a vital anatomical feature in certain invertebrates, playing a key role in the efficient absorption of nutrients. Its presence underscores the importance of anatomical adaptations in the evolution of digestive systems, reflecting the diverse strategies organisms have developed to meet their nutritional needs. Understanding the structure and function of the typhlosole not only sheds light on the biology of these organisms but also highlights the intricate connections between anatomy, ecology, and evolution.
Typhlosole[edit]
-
Tiflossole de oligochaeta