Flutter valve: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Flutter Valve | |||
The ''' | The '''flutter valve''', also known as the '''Heimlich valve''', is a one-way valve used in medical settings to allow air or fluid to escape from a body cavity while preventing it from re-entering. It is commonly used in the management of [[pneumothorax]] and other conditions where air or fluid needs to be evacuated from the [[pleural cavity]]. | ||
==Design and Function== | ==Design and Function== | ||
The | |||
[[File:Heimlich_valve.GIF|thumb|right|Diagram of a Heimlich valve]] | |||
The flutter valve is typically constructed from a flexible material, such as rubber or silicone, and consists of a flat or cylindrical tube with a slit or flap that opens to allow air or fluid to pass through in one direction. The valve closes when pressure attempts to reverse the flow, thus preventing backflow. | |||
The valve is often attached to a chest tube, which is inserted into the pleural space. As the patient breathes, air or fluid is expelled through the valve, reducing pressure in the pleural cavity and allowing the lung to re-expand. | |||
==Clinical Applications== | ==Clinical Applications== | ||
The flutter valve is primarily used in the treatment of [[pneumothorax]], a condition where air accumulates in the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse. It is also used in cases of [[pleural effusion]], where fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity. | |||
[[File:Heimlich-ventil-foto.jpg|thumb|left|Photograph of a Heimlich valve in use]] | |||
In emergency situations, the flutter valve can be a lifesaving device, allowing for rapid decompression of the pleural space. It is often used in pre-hospital settings, such as by paramedics, and in military medicine. | |||
==Advantages== | ==Advantages== | ||
The | |||
The flutter valve offers several advantages: | |||
* '''Portability''': It is lightweight and compact, making it easy to transport and use in various settings. | |||
* '''Simplicity''': The design is straightforward, requiring minimal training to use effectively. | |||
* '''Safety''': By preventing backflow, the valve reduces the risk of infection and further complications. | |||
==Limitations== | ==Limitations== | ||
While the flutter valve is effective in many situations, it has limitations: | |||
* '''Limited to specific conditions''': It is not suitable for all types of chest injuries or conditions. | |||
* '''Potential for blockage''': The valve can become blocked by thick fluids or debris, necessitating careful monitoring. | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
[[ | * [[Pneumothorax]] | ||
[[ | * [[Pleural effusion]] | ||
[[ | * [[Chest tube]] | ||
* [[One-way valve]] | |||
[[Category:Medical devices]] | |||
[[Category:Respiratory system procedures]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:19, 21 February 2025
Flutter Valve
The flutter valve, also known as the Heimlich valve, is a one-way valve used in medical settings to allow air or fluid to escape from a body cavity while preventing it from re-entering. It is commonly used in the management of pneumothorax and other conditions where air or fluid needs to be evacuated from the pleural cavity.
Design and Function[edit]

The flutter valve is typically constructed from a flexible material, such as rubber or silicone, and consists of a flat or cylindrical tube with a slit or flap that opens to allow air or fluid to pass through in one direction. The valve closes when pressure attempts to reverse the flow, thus preventing backflow.
The valve is often attached to a chest tube, which is inserted into the pleural space. As the patient breathes, air or fluid is expelled through the valve, reducing pressure in the pleural cavity and allowing the lung to re-expand.
Clinical Applications[edit]
The flutter valve is primarily used in the treatment of pneumothorax, a condition where air accumulates in the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse. It is also used in cases of pleural effusion, where fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity.
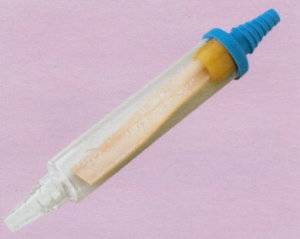
In emergency situations, the flutter valve can be a lifesaving device, allowing for rapid decompression of the pleural space. It is often used in pre-hospital settings, such as by paramedics, and in military medicine.
Advantages[edit]
The flutter valve offers several advantages:
- Portability: It is lightweight and compact, making it easy to transport and use in various settings.
- Simplicity: The design is straightforward, requiring minimal training to use effectively.
- Safety: By preventing backflow, the valve reduces the risk of infection and further complications.
Limitations[edit]
While the flutter valve is effective in many situations, it has limitations:
- Limited to specific conditions: It is not suitable for all types of chest injuries or conditions.
- Potential for blockage: The valve can become blocked by thick fluids or debris, necessitating careful monitoring.