Broadband: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Internet-stub}} | {{Internet-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Fixed_broadband_subscriptions_(per_100_people),_OWID.svg|Fixed broadband subscriptions per 100 people | |||
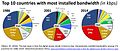
File:GlobalBandwidthConcentration.jpg|Global Bandwidth Concentration | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:16, 18 February 2025
Broadband refers to a high-speed Internet connection that is always on and faster than the traditional dial-up access. Broadband includes several high-speed transmission technologies such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Fiber, Wireless, Satellite, and Cable. The breadth of the band in broadband communication is wide, allowing for the transmission of multiple signals and traffic types simultaneously.
Types of Broadband[edit]
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)[edit]
DSL is a wireline transmission technology that transmits data faster over traditional copper telephone lines already installed to homes and businesses. DSL-based broadband provides transmission speeds ranging from several hundred Kbps to millions of bits per second (Mbps). The availability and speed of your DSL service may depend on the distance from your home or business to the closest telephone company facility.
Fiber-optic Communication[edit]
Fiber-optic broadband offers the highest speed internet connection by using light to transmit data over fiber cables. This technology can provide internet access with speeds up to 1 Gbps or higher.
Wireless[edit]
Wireless broadband connects a home or business to the Internet using a radio link between the customer’s location and the service provider’s facility. Wireless broadband can be mobile or fixed.
Satellite[edit]
Satellite broadband is another form of wireless broadband, and is particularly useful for serving remote or sparsely populated areas. Downstream and upstream speeds for satellite broadband depend on several factors, including the provider and service package purchased, the consumer’s line of sight to the orbiting satellite, and the weather.
Cable Modem[edit]
Cable broadband technology uses the coaxial cable that carries television signals into the home to provide Internet access. Speeds with cable broadband can vary depending on the amount of traffic or congestion on the network.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
Broadband internet access has transformed the way internet is used. It supports high-speed data transmission, enables streaming of video and music, supports high-quality voice and video calls, and much more. However, the availability of broadband varies by geographic location, with rural areas often having fewer options compared to urban areas. The cost of broadband can also be a barrier for some households.
Future of Broadband[edit]
The future of broadband lies in the continuous development of technologies and infrastructure to support faster and more reliable internet connections. Innovations such as 5G wireless technology and further expansion of fiber-optic networks are expected to provide even faster and more robust internet connections in the future.
-
Fixed broadband subscriptions per 100 people
-
Global Bandwidth Concentration