Ferruginous body: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Occupational diseases]] | [[Category:Occupational diseases]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
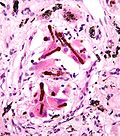
File:ferruginous_body.jpg|Ferruginous body | |||
File:Asbestosis_high_mag.jpg|Asbestosis high magnification | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:09, 17 February 2025
Ferruginous body refers to a microscopic, rod-like structure often found within the lung tissues, which is coated with iron-containing (ferruginous) material. These bodies are typically associated with the inhalation of certain types of dusts, most notably asbestos fibers, and are considered markers of exposure to these materials. The presence of ferruginous bodies can be indicative of various pulmonary conditions, including asbestosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and mesothelioma.
Formation[edit]
Ferruginous bodies form when inhaled fibers, such as asbestos, become coated with a protein-rich material containing iron. This coating process occurs within the lungs and is a response by the body to the presence of foreign materials. The iron coating is thought to be derived from ferritin, an iron-storage protein, which attempts to neutralize the fibers by encapsulating them. However, this process does not render the fibers harmless and instead serves as a marker of exposure.
Health Implications[edit]
The presence of ferruginous bodies in lung tissue is a significant indicator of past exposure to hazardous materials like asbestos. While the bodies themselves are not harmful, their presence suggests that the individual has been exposed to materials that can cause serious lung diseases. Diseases associated with ferruginous bodies include:
- Asbestosis: A lung disease resulting from the inhalation of asbestos particles, leading to lung scarring and breathing difficulties.
- Mesothelioma: A rare form of cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, chest, abdomen, and heart, and is strongly linked to asbestos exposure.
- Lung cancer: Exposure to asbestos and other materials that can lead to the formation of ferruginous bodies is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.
Diagnosis[edit]
The identification of ferruginous bodies is typically done through histological examination of lung tissue samples obtained via biopsy. Special staining techniques, such as Prussian blue staining, are used to highlight the iron content of the bodies, making them more visible under a microscope.
Prevention and Management[edit]
Preventing exposure to asbestos and other hazardous materials is key to reducing the risk of developing lung diseases associated with ferruginous bodies. This includes adhering to safety guidelines and regulations in workplaces where exposure to such materials is possible. Management of conditions associated with ferruginous bodies involves treating the symptoms and complications of the diseases, as there is no cure for conditions like asbestosis and mesothelioma once they have developed.
See Also[edit]
-
Ferruginous body
-
Asbestosis high magnification