Etoperidone: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An antidepressant drug}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477318123 | |||
| image = Etoperidone_structure.svg | |||
| image2 = | |||
| width = 200 | |||
| alt = | |||
| caption = Chemical structure of Etoperidone | |||
}} | |||
'''Etoperidone''' is a [[pharmaceutical drug]] that was developed as an [[antidepressant]]. It belongs to the class of drugs known as [[serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors]] (SARIs). Although it was never marketed in the United States, it has been used in some European countries. | |||
== | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Etoperidone | Etoperidone functions primarily as a [[serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor]], which means it blocks the reuptake of [[serotonin]] in the brain, increasing its availability in the synaptic cleft. This action is believed to contribute to its antidepressant effects. Additionally, etoperidone has been shown to have affinity for various [[neurotransmitter]] receptors, including [[alpha-adrenergic receptor|alpha-adrenergic]], [[dopamine receptor|dopaminergic]], and [[histamine receptor|histaminergic]] receptors. | ||
== | ==Clinical Use== | ||
Etoperidone was primarily used in the treatment of [[major depressive disorder]]. Its efficacy in alleviating symptoms of depression was comparable to other antidepressants available at the time. However, due to the development of newer antidepressants with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects, etoperidone is not commonly used today. | |||
== | ==Side Effects== | ||
The side effects of etoperidone are similar to those of other antidepressants in its class. Common side effects include [[drowsiness]], [[dry mouth]], and [[dizziness]]. Some patients may experience [[gastrointestinal disturbances]] such as [[nausea]] and [[vomiting]]. As with other antidepressants, there is a risk of [[serotonin syndrome]] if taken in combination with other serotonergic drugs. | |||
== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Etoperidone | Etoperidone's mechanism of action involves the inhibition of serotonin reuptake, which increases serotonin levels in the brain. This is thought to improve mood and alleviate depressive symptoms. Additionally, its antagonistic effects on various neurotransmitter receptors may contribute to its overall therapeutic profile. | ||
==Development and History== | |||
Etoperidone was developed in the 1970s by the pharmaceutical company Angelini. It was part of a wave of new antidepressants that sought to improve upon the side effect profiles of earlier drugs. Despite its initial promise, etoperidone was overshadowed by the development of [[selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors]] (SSRIs) and other newer classes of antidepressants. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Antidepressant]] | |||
* [[Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor]] | |||
* [[Major depressive disorder]] | |||
* [[Serotonin syndrome]] | |||
[[Category:Antidepressants]] | [[Category:Antidepressants]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors]] | ||
[[Category:Drugs not assigned an ATC code]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:34, 23 March 2025
An antidepressant drug
| Etoperidone | |
|---|---|
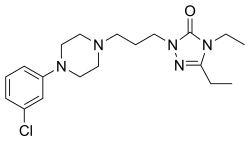
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Etoperidone is a pharmaceutical drug that was developed as an antidepressant. It belongs to the class of drugs known as serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs). Although it was never marketed in the United States, it has been used in some European countries.
Pharmacology[edit]
Etoperidone functions primarily as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor, which means it blocks the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, increasing its availability in the synaptic cleft. This action is believed to contribute to its antidepressant effects. Additionally, etoperidone has been shown to have affinity for various neurotransmitter receptors, including alpha-adrenergic, dopaminergic, and histaminergic receptors.
Clinical Use[edit]
Etoperidone was primarily used in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Its efficacy in alleviating symptoms of depression was comparable to other antidepressants available at the time. However, due to the development of newer antidepressants with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects, etoperidone is not commonly used today.
Side Effects[edit]
The side effects of etoperidone are similar to those of other antidepressants in its class. Common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness. Some patients may experience gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and vomiting. As with other antidepressants, there is a risk of serotonin syndrome if taken in combination with other serotonergic drugs.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Etoperidone's mechanism of action involves the inhibition of serotonin reuptake, which increases serotonin levels in the brain. This is thought to improve mood and alleviate depressive symptoms. Additionally, its antagonistic effects on various neurotransmitter receptors may contribute to its overall therapeutic profile.
Development and History[edit]
Etoperidone was developed in the 1970s by the pharmaceutical company Angelini. It was part of a wave of new antidepressants that sought to improve upon the side effect profiles of earlier drugs. Despite its initial promise, etoperidone was overshadowed by the development of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and other newer classes of antidepressants.