Foreign body: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Foreign body | |||
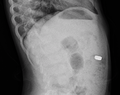
| image = [[File:Foreign_Body.jpg|250px]] | |||
| alt = X-ray showing a foreign body | |||
| caption = X-ray of a foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract | |||
| field = [[Emergency medicine]], [[Otolaryngology]], [[Gastroenterology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pain]], [[swelling]], [[obstruction]], [[infection]] | |||
| complications = [[Perforation]], [[infection]], [[bleeding]], [[obstruction]] | |||
| onset = Sudden | |||
| duration = Variable, depending on location and intervention | |||
| causes = Ingestion, inhalation, insertion, trauma | |||
| risks = [[Children]], [[elderly]], [[dementia]], [[psychiatric disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]], [[CT scan]], [[endoscopy]] | |||
| differential = [[Tumor]], [[abscess]], [[hematoma]] | |||
| prevention = Supervision, education, safety measures | |||
| treatment = [[Endoscopic removal]], [[surgery]], [[observation]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with prompt treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in children, less common in adults | |||
}} | |||
'''Foreign Body''' refers to any object originating outside the body that is introduced into it, either accidentally or deliberately. These objects can enter the body through various means such as ingestion, inhalation, or penetration of the skin or mucous membranes. The presence of a foreign body can lead to various medical complications, including infection, tissue damage, and allergic reactions. The management and treatment of foreign bodies depend on their location, type, and the symptoms they cause. | '''Foreign Body''' refers to any object originating outside the body that is introduced into it, either accidentally or deliberately. These objects can enter the body through various means such as ingestion, inhalation, or penetration of the skin or mucous membranes. The presence of a foreign body can lead to various medical complications, including infection, tissue damage, and allergic reactions. The management and treatment of foreign bodies depend on their location, type, and the symptoms they cause. | ||
==Types of Foreign Bodies== | ==Types of Foreign Bodies== | ||
Foreign bodies can be classified based on their nature and the route through which they enter the body: | Foreign bodies can be classified based on their nature and the route through which they enter the body: | ||
* '''Ingested Foreign Bodies''': These are objects swallowed accidentally. Common examples include fish bones, coins, and small toys. Ingested foreign bodies can cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain and obstruction. | * '''Ingested Foreign Bodies''': These are objects swallowed accidentally. Common examples include fish bones, coins, and small toys. Ingested foreign bodies can cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain and obstruction. | ||
* '''Inhaled Foreign Bodies''': Objects that enter the respiratory tract are known as inhaled foreign bodies. Small toys, food particles, and other small objects can be inhaled, especially by children, leading to coughing, wheezing, and potentially life-threatening respiratory distress. | * '''Inhaled Foreign Bodies''': Objects that enter the respiratory tract are known as inhaled foreign bodies. Small toys, food particles, and other small objects can be inhaled, especially by children, leading to coughing, wheezing, and potentially life-threatening respiratory distress. | ||
* '''Penetrating Foreign Bodies''': These are objects that penetrate the skin or mucous membranes, such as splinters, glass shards, and metal fragments. Depending on their location, penetrating foreign bodies can cause minor to severe injuries. | * '''Penetrating Foreign Bodies''': These are objects that penetrate the skin or mucous membranes, such as splinters, glass shards, and metal fragments. Depending on their location, penetrating foreign bodies can cause minor to severe injuries. | ||
* '''Ocular Foreign Bodies''': Objects that enter the eye, such as metal particles, wood shavings, and dust, can cause irritation, redness, and potentially impair vision. | * '''Ocular Foreign Bodies''': Objects that enter the eye, such as metal particles, wood shavings, and dust, can cause irritation, redness, and potentially impair vision. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of a foreign body depend on its location and nature. Common symptoms include: | The symptoms of a foreign body depend on its location and nature. Common symptoms include: | ||
* Pain or discomfort in the affected area | * Pain or discomfort in the affected area | ||
* Difficulty swallowing or breathing | * Difficulty swallowing or breathing | ||
| Line 17: | Line 33: | ||
* Bleeding or discharge from the entry point | * Bleeding or discharge from the entry point | ||
* Visible object in the skin or eye | * Visible object in the skin or eye | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of a foreign body often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. X-rays are commonly used to locate metallic objects, while CT scans and MRIs can provide detailed images of non-metallic objects and their effects on surrounding tissues. | Diagnosis of a foreign body often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. X-rays are commonly used to locate metallic objects, while CT scans and MRIs can provide detailed images of non-metallic objects and their effects on surrounding tissues. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment varies based on the type and location of the foreign body: | Treatment varies based on the type and location of the foreign body: | ||
* '''Ingested Foreign Bodies''': Many ingested objects pass through the digestive tract without causing harm. However, objects causing obstruction or symptoms may require endoscopic removal. | * '''Ingested Foreign Bodies''': Many ingested objects pass through the digestive tract without causing harm. However, objects causing obstruction or symptoms may require endoscopic removal. | ||
* '''Inhaled Foreign Bodies''': Removal of inhaled objects is usually performed using bronchoscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the airways to locate and remove the object. | * '''Inhaled Foreign Bodies''': Removal of inhaled objects is usually performed using bronchoscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the airways to locate and remove the object. | ||
* '''Penetrating Foreign Bodies''': Superficial objects may be removed in a healthcare provider's office, while deeper or more dangerous objects may require surgical intervention. | * '''Penetrating Foreign Bodies''': Superficial objects may be removed in a healthcare provider's office, while deeper or more dangerous objects may require surgical intervention. | ||
* '''Ocular Foreign Bodies''': Minor ocular foreign bodies can be flushed out with saline solution, while others may require removal by an eye care professional. | * '''Ocular Foreign Bodies''': Minor ocular foreign bodies can be flushed out with saline solution, while others may require removal by an eye care professional. | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventive measures include keeping small objects out of reach of children, wearing protective eyewear during activities that could result in eye injuries, and being cautious when eating foods that may contain bones or other hard particles. | Preventive measures include keeping small objects out of reach of children, wearing protective eyewear during activities that could result in eye injuries, and being cautious when eating foods that may contain bones or other hard particles. | ||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
If not properly managed, foreign bodies can lead to complications such as infections, abscess formation, and damage to internal organs or tissues. Timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent serious outcomes. | If not properly managed, foreign bodies can lead to complications such as infections, abscess formation, and damage to internal organs or tissues. Timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent serious outcomes. | ||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:CoinAP.jpg|Coin AP view | |||
File:CoinL.jpg|Coin lateral view | |||
File:9mmbatteryintestines.png|9mm battery in intestines | |||
File:9mmbatteryintestineslt.png|9mm battery in intestines lateral view | |||
File:BatteriesInStomach.jpg|Batteries in stomach | |||
File:ButtonBatteryIngestion.png|Button battery ingestion | |||
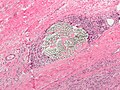
File:Suture_micrograph.jpg|Suture micrograph | |||
File:Embolization_kidney.jpg|Embolization kidney | |||
File:Pulmonary_talcosis_low_mag_cropped.jpg|Pulmonary talcosis low magnification | |||
File:Bottle_top_swallowed_by_dog_2.JPG|Bottle top swallowed by dog | |||
File:X-ray_Needle_swallowed_by_cat.JPG|X-ray of needle swallowed by cat | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Medical terminology]] | [[Category:Medical terminology]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | [[Category:Pediatrics]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:19, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Foreign body | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, obstruction, infection |
| Complications | Perforation, infection, bleeding, obstruction |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Variable, depending on location and intervention |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Ingestion, inhalation, insertion, trauma |
| Risks | Children, elderly, dementia, psychiatric disorders |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, CT scan, endoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Tumor, abscess, hematoma |
| Prevention | Supervision, education, safety measures |
| Treatment | Endoscopic removal, surgery, observation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with prompt treatment |
| Frequency | Common in children, less common in adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
Foreign Body refers to any object originating outside the body that is introduced into it, either accidentally or deliberately. These objects can enter the body through various means such as ingestion, inhalation, or penetration of the skin or mucous membranes. The presence of a foreign body can lead to various medical complications, including infection, tissue damage, and allergic reactions. The management and treatment of foreign bodies depend on their location, type, and the symptoms they cause.
Types of Foreign Bodies[edit]
Foreign bodies can be classified based on their nature and the route through which they enter the body:
- Ingested Foreign Bodies: These are objects swallowed accidentally. Common examples include fish bones, coins, and small toys. Ingested foreign bodies can cause symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain and obstruction.
- Inhaled Foreign Bodies: Objects that enter the respiratory tract are known as inhaled foreign bodies. Small toys, food particles, and other small objects can be inhaled, especially by children, leading to coughing, wheezing, and potentially life-threatening respiratory distress.
- Penetrating Foreign Bodies: These are objects that penetrate the skin or mucous membranes, such as splinters, glass shards, and metal fragments. Depending on their location, penetrating foreign bodies can cause minor to severe injuries.
- Ocular Foreign Bodies: Objects that enter the eye, such as metal particles, wood shavings, and dust, can cause irritation, redness, and potentially impair vision.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of a foreign body depend on its location and nature. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Coughing or wheezing
- Bleeding or discharge from the entry point
- Visible object in the skin or eye
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a foreign body often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. X-rays are commonly used to locate metallic objects, while CT scans and MRIs can provide detailed images of non-metallic objects and their effects on surrounding tissues.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment varies based on the type and location of the foreign body:
- Ingested Foreign Bodies: Many ingested objects pass through the digestive tract without causing harm. However, objects causing obstruction or symptoms may require endoscopic removal.
- Inhaled Foreign Bodies: Removal of inhaled objects is usually performed using bronchoscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the airways to locate and remove the object.
- Penetrating Foreign Bodies: Superficial objects may be removed in a healthcare provider's office, while deeper or more dangerous objects may require surgical intervention.
- Ocular Foreign Bodies: Minor ocular foreign bodies can be flushed out with saline solution, while others may require removal by an eye care professional.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures include keeping small objects out of reach of children, wearing protective eyewear during activities that could result in eye injuries, and being cautious when eating foods that may contain bones or other hard particles.
Complications[edit]
If not properly managed, foreign bodies can lead to complications such as infections, abscess formation, and damage to internal organs or tissues. Timely medical intervention is crucial to prevent serious outcomes.
Gallery[edit]
-
Coin AP view
-
Coin lateral view
-
9mm battery in intestines
-
9mm battery in intestines lateral view
-
Batteries in stomach
-
Button battery ingestion
-
Suture micrograph
-
Embolization kidney
-
Pulmonary talcosis low magnification
-
Bottle top swallowed by dog
-
X-ray of needle swallowed by cat