RUNX2: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Genetics-stub}} | {{Genetics-stub}} | ||
== RUNX2 == | |||
<gallery> | |||
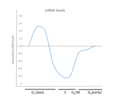
File:Oscillations_of_Runx2_mRNA_levels.png|Oscillations of Runx2 mRNA levels | |||
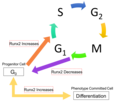
File:Schematic_of_Runx2_Levels_During_Cell_Cycle_Progression.png|Schematic of Runx2 Levels During Cell Cycle Progression | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:58, 25 February 2025
RUNX2, also known as Runt-related transcription factor 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUNX2 gene. This protein plays a critical role in the differentiation of osteoblasts, cells that are responsible for bone formation. Due to its pivotal role in skeletal development, mutations in RUNX2 are associated with a variety of bone-related disorders.
Function[edit]
RUNX2 is a key transcription factor in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis. It is essential for the maturation of osteoblasts and is involved in the expression of several genes related to bone formation, including osteocalcin, bone sialoprotein, and osteopontin. RUNX2 functions by binding to specific DNA sequences, thereby regulating the activity of genes important for bone development and maintenance.
Genetic Structure[edit]
The RUNX2 gene is located on the human chromosome 6p21. It consists of multiple exons that encode the RUNX2 protein. This protein contains a Runt domain, which is involved in DNA binding and protein-protein interactions, crucial for its function as a transcription factor.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to skeletal disorders. The most well-known condition associated with RUNX2 mutations is Cleidocranial Dysplasia (CCD), a rare genetic disorder characterized by delayed closure of cranial sutures, abnormal development of clavicles, and dental anomalies. Patients with CCD exhibit a wide range of skeletal abnormalities, underscoring the importance of RUNX2 in bone development and maintenance.
Research and Applications[edit]
Research on RUNX2 has expanded our understanding of bone biology and the molecular mechanisms underlying bone diseases. This knowledge has potential applications in developing therapeutic strategies for bone-related conditions. For instance, manipulating RUNX2 activity could offer new approaches to enhancing bone regeneration and treating osteoporosis.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
RUNX2[edit]
-
Oscillations of Runx2 mRNA levels
-
Schematic of Runx2 Levels During Cell Cycle Progression