Beat (acoustics): Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{music-stub}} | {{music-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Beat (acoustics) == | |||
<gallery> | |||
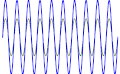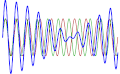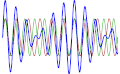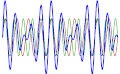
File:Beating_Frequency.svg|Beating Frequency | |||
File:WaveInterference.gif|Wave Interference | |||
File:Binaural_beats.svg|Binaural Beats | |||
File:Binaural_beat_lossless_new.wav|Binaural Beat Lossless New | |||
File:Pure_Alpha_Waves_7_to_12,9_Hz_Binaural_Beats_V3.wav|Pure Alpha Waves 7 to 12.9 Hz Binaural Beats V3 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:55, 25 February 2025
Beat (acoustics) is a term used in acoustics to describe the interference pattern between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, perceived as a periodic variation in volume whose rate is the difference of the two frequencies.
Overview[edit]
When tuning instruments that can produce sustained tones, beats can be readily recognized. Tuning two tones to a unison will present a peculiar effect: when the two tones are close in pitch but not identical, the difference in frequency generates the beating. The volume varies like in a tremolo as the sounds alternately interfere constructively and destructively. As the two tones gradually approach unison, the beating slows down and may become so slow as to be imperceptible.
Mathematical representation[edit]
In terms of mathematics, the physical interpretation of the "beat" phenomenon can be modelled by the superposition principle for two waves of different frequencies. The beat frequency is equal to the absolute difference between the frequencies of the two waves.
Applications[edit]
In music, beats are used to create rhythm. In healthcare, the concept of beats is used in cardiology to understand the rhythm of the heart. In physics, beats are used to measure the frequency difference of two sounds.
See also[edit]
Beat (acoustics)[edit]
-
Beating Frequency
-
Wave Interference
-
Binaural Beats
-
Binaural Beat Lossless New
-
Pure Alpha Waves 7 to 12.9 Hz Binaural Beats V3