Colloidal gold: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery caption="Colloidal_gold"> | |||
File:Gold255.jpg|Colloidal gold solution | |||
File:Gold_Colloid_of_varying_size.jpg|Gold colloid of varying size | |||
File:Vintage_cranberry_glass.jpg|Vintage cranberry glass | |||
File:Cross_section_vs._wavelength_of_Au_nanoparticle_cropped.png|Cross section vs. wavelength of Au nanoparticle | |||
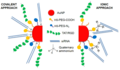
File:tumor_targeting.png|Gold nanoparticles for tumor targeting | |||
File:Gold_siRNA_nanoparticles.png|Gold siRNA nanoparticles | |||
File:Gold_nanoparticles_as_indicators.jpg|Gold nanoparticles as indicators | |||
File:Gold_nanoparticle_Zeta-potential.png|Gold nanoparticle Zeta-potential | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:45, 18 February 2025
Colloidal gold is a suspension, or colloid, of submicroscopic gold particles, typically in water. The liquid is usually either an intense red colour (for particles less than 100 nm), or a dirty yellowish colour (for larger particles). The particles themselves are often spherical.
History[edit]
Gold has been used in medicine since ancient times, and colloidal gold was reportedly used by Paracelsus in the 16th century. In the 19th century, colloidal gold was used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, and other conditions.
Preparation[edit]
Colloidal gold is prepared by reducing gold ions with a reducing agent. The gold particles are then stabilized by a surfactant to prevent them from aggregating. The size and shape of the particles can be controlled by varying the conditions of the reaction.
Medical uses[edit]
Colloidal gold has been used in a variety of medical applications. It has been used as a contrast agent in electron microscopy, and as a tracer in immunology and histology. It has also been used in photothermal therapy for cancer treatment.
Safety[edit]
While colloidal gold is generally considered safe for topical use, ingestion can lead to gold poisoning. Symptoms of gold poisoning include skin rash, diarrhea, and neurological symptoms.
See also[edit]
- Colloidal_gold
-
Colloidal gold solution
-
Gold colloid of varying size
-
Vintage cranberry glass
-
Cross section vs. wavelength of Au nanoparticle
-
Gold nanoparticles for tumor targeting
-
Gold siRNA nanoparticles
-
Gold nanoparticles as indicators
-
Gold nanoparticle Zeta-potential