Apocynin: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Apocynin gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
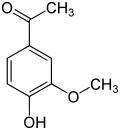
File:Acetovanillone.svg|Acetovanillone | |||
File:Apocynin-from-xtal-Mercury-3D-bs.png|Apocynin from crystal Mercury 3D ball-and-stick | |||
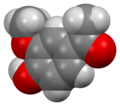
File:Apocynin-from-xtal-Mercury-3D-sf.png|Apocynin from crystal Mercury 3D space-filling | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 19:02, 16 March 2025
Apocynin is a natural organic compound that is structurally classified as a catechol. It is derived from the roots of the Picrorhiza kurroa plant, which is native to the mountainous regions of India, Nepal, and Tibet. Apocynin has been used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine for centuries, primarily for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Apocynin is a simple molecule, consisting of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups (OH) and one methoxy group (OCH3). Its chemical formula is C9H10O4 and its molecular weight is 182.17 g/mol. It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature and is soluble in water, ethanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Pharmacological Actions[edit]
Apocynin has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects in a variety of medical conditions. Its primary mechanism of action is the inhibition of NADPH oxidase, an enzyme complex that generates reactive oxygen species (ROS). By inhibiting NADPH oxidase, apocynin reduces oxidative stress, which is implicated in many diseases.
Anti-inflammatory Effects[edit]
Apocynin has been shown to reduce inflammation in several experimental models. It inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), and it suppresses the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B), a key regulator of the inflammatory response.
Antioxidant Effects[edit]
By inhibiting NADPH oxidase, apocynin also exerts antioxidant effects. It reduces the production of ROS, which can damage cells and tissues, and it increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx).
Potential Therapeutic Applications[edit]
Research on apocynin has suggested potential applications in a variety of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disease, asthma, and cancer. However, most of this research is preclinical, and further studies are needed to confirm these findings and to determine the optimal dosage and administration of apocynin.
Safety and Toxicity[edit]
Apocynin is generally considered safe at therapeutic doses. However, like all drugs, it can cause side effects and interactions, and it should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider. Potential side effects include gastrointestinal upset, skin rash, and allergic reactions.
See Also[edit]
Apocynin gallery[edit]
-
Acetovanillone
-
Apocynin from crystal Mercury 3D ball-and-stick
-
Apocynin from crystal Mercury 3D space-filling