Harmala alkaloid: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | [[Category:Pharmacology]] | ||
{{pharmacology-stub}} | {{pharmacology-stub}} | ||
== Harmala_alkaloid == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Peganum_harmala1.jpg|Peganum harmala plant | |||
File:Harmaline_Harmine.jpg|Harmaline and Harmine | |||
File:Harmine_structure.svg|Harmine structure | |||
File:Harmaline_structure.svg|Harmaline structure | |||
File:Harmalol.svg|Harmalol structure | |||
File:Tetrahydroharmine_structure.svg|Tetrahydroharmine structure | |||
File:Harmalane.svg|Harmalane structure | |||
File:Isoharmine.svg|Isoharmine structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:57, 27 February 2025
Harmala Alkaloid
Harmala alkaloids are a group of alkaloids that are derived from the Peganum harmala plant, also known as Syrian rue. These alkaloids have been used for centuries in traditional medicine and have been the subject of numerous scientific studies due to their potential therapeutic effects.
History[edit]
The use of Peganum harmala and its alkaloids dates back to ancient times. The plant is native to the Middle East and has been used in traditional medicine for its sedative, analgesic, and antimicrobial properties. The primary alkaloids found in Peganum harmala are harmine, harmaline, and tetrahydroharmine.
Chemistry[edit]
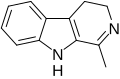
Harmala alkaloids are beta-carboline alkaloids. They are characterized by a tricyclic structure, which includes a pyridine ring fused with a benzene ring and a five-membered ring with two nitrogen atoms. The three main harmala alkaloids - harmine, harmaline, and tetrahydroharmine - differ in their substitution patterns on the beta-carboline core.
Pharmacology[edit]
Harmala alkaloids are known to have a wide range of pharmacological effects. They are most notably MAO inhibitors, which means they can inhibit the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. This can lead to increased levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, which can have various effects on mood, cognition, and behavior.
Potential Therapeutic Uses[edit]
Due to their pharmacological properties, harmala alkaloids have been investigated for potential therapeutic uses. Some studies have suggested that they may have potential in the treatment of conditions such as depression, Parkinson's disease, and certain types of cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand their potential benefits and risks.
Safety and Toxicity[edit]
While harmala alkaloids have potential therapeutic uses, they can also be toxic in high doses. Symptoms of harmala alkaloid poisoning can include nausea, vomiting, hallucinations, and in severe cases, seizures or death. Therefore, they should be used with caution and under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
See Also[edit]
Harmala_alkaloid[edit]
-
Peganum harmala plant
-
Harmaline and Harmine
-
Harmine structure
-
Harmaline structure
-
Harmalol structure
-
Tetrahydroharmine structure
-
Harmalane structure
-
Isoharmine structure