NEFA (drug): Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Category:Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]] | [[Category:Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | [[Category:Pharmacology]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
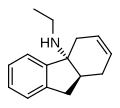
File:NEFA.svg|NEFA chemical structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:23, 3 March 2025
NEFA (drug)
NEFA is a pharmacological agent that is classified as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is primarily used in the treatment of conditions such as arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory disorders.
Pharmacology[edit]
NEFA works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, chemicals that cause inflammation, pain, and fever in the body. It does this by blocking the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins. There are two types of COX enzymes: COX-1 and COX-2. NEFA is a non-selective inhibitor, meaning it blocks both COX-1 and COX-2.
Clinical Use[edit]
NEFA is used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. This makes it effective in treating conditions such as arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory disorders. It is also used to manage acute pain and menstrual cramps.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all NSAIDs, NEFA can cause side effects. The most common of these include stomach upset, heartburn, dizziness, and headache. More serious side effects can include stomach bleeding, kidney problems, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
Contraindications[edit]
NEFA should not be used by individuals with a history of allergic reaction to aspirin or other NSAIDs. It is also contraindicated in patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding, as well as in patients with severe kidney disease.
See Also[edit]
-
NEFA chemical structure