Glandular metaplasia: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
[[Category:Endocrinology]] | [[Category:Endocrinology]] | ||
{{anatomy-stub}} | {{anatomy-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
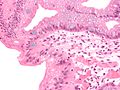
File:Barretts_alcian_blue.jpg|Glandular metaplasia | |||
File:Barretts_esophagus_alcian_blue_high_mag.jpg|Glandular metaplasia | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:57, 18 February 2025
Glandular branches are specialized structures in the body that are part of the larger endocrine system. They are responsible for the production and secretion of hormones that regulate a wide range of bodily functions.
Anatomy and Function[edit]
Glandular branches are found in various glands throughout the body. These include the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland, the adrenal glands, and the pancreas. Each of these glands contains specialized cells that produce specific hormones.
The hormones produced by glandular branches are released into the bloodstream and transported to target cells or organs in the body. These hormones act as chemical messengers, triggering specific responses in the target cells.
Types of Glandular Branches[edit]
There are several types of glandular branches, each associated with a specific gland and hormone production.
Pituitary Gland[edit]
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the "master gland" because it controls the function of many other glands in the body. It has two main parts: the anterior pituitary and the posterior pituitary. Each part produces different hormones.
Thyroid Gland[edit]
The thyroid gland is located in the neck and produces thyroid hormones, which regulate the body's metabolism.
Adrenal Glands[edit]
The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys and produce a variety of hormones, including cortisol and adrenaline.
Pancreas[edit]
The pancreas is both an endocrine and exocrine gland. As an endocrine gland, it produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
Disorders of Glandular Branches[edit]
Disorders of glandular branches can lead to a variety of health problems. These can include diabetes, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and Addison's disease. Treatment for these disorders often involves hormone replacement therapy.
See Also[edit]
-
Glandular metaplasia
-
Glandular metaplasia