Sphingomyelin: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Lipids]] | [[Category:Lipids]] | ||
{{biochemistry-stub}} | {{biochemistry-stub}} | ||
== Sphingomyelin == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Sphingolipids_general_structures.png|General structures of sphingolipids | |||
File:Sphingomyelin_core_structure_colored.svg|Core structure of sphingomyelin | |||
File:Top-down_Sphingomyelin.png|Top-down view of sphingomyelin | |||
File:Sphingomyelin_Synthesis.png|Sphingomyelin synthesis pathway | |||
File:Sphingomyelin-horizontal-3D-balls.png|3D ball model of sphingomyelin | |||
File:Sphingomyelin-horizontal-2D-skeletal.png|2D skeletal formula of sphingomyelin | |||
File:Ceramid.svg|Structure of ceramide | |||
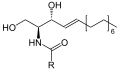
File:Sphingosine_structure.svg|Structure of sphingosine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:50, 18 February 2025
Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It was discovered by German chemist Johannes Thudichum in the brain in 1884.
Structure[edit]
Sphingomyelin is composed of a phosphocholine molecule, a sphingosine molecule, and a fatty acid. The fatty acid can vary in chain length and saturation level. The structure of sphingomyelin is similar to phosphatidylcholine, but instead of glycerol backbone, sphingomyelin has a sphingosine backbone.
Function[edit]
Sphingomyelin plays a crucial role in cell signaling and apoptosis. It is also a major component of the myelin sheath, a protective layer that surrounds the axons of neurons. This sheath allows for efficient conduction of electrical impulses along the nerve cells.
Metabolism[edit]
Sphingomyelin is synthesized in the Golgi apparatus, where it is also converted into ceramide by the enzyme sphingomyelinase. Ceramide can then be further metabolized into other sphingolipids, such as sphingosine-1-phosphate, which has important signaling functions.
Disease relevance[edit]
Defects in sphingomyelin metabolism can lead to several diseases, such as Niemann-Pick disease, a lysosomal storage disease characterized by the accumulation of sphingomyelin in cells.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Sphingomyelin[edit]
-
General structures of sphingolipids
-
Core structure of sphingomyelin
-
Top-down view of sphingomyelin
-
Sphingomyelin synthesis pathway
-
3D ball model of sphingomyelin
-
2D skeletal formula of sphingomyelin
-
Structure of ceramide
-
Structure of sphingosine