Metfendrazine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
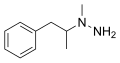
File:Metfendrazine structure.svg|Metfendrazine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:11, 20 February 2025
Metfendrazine is a stimulant drug which was developed in the 1960s. It is related to phenmetrazine, a once-popular stimulant that was later banned due to abuse potential. Metfendrazine is less well-known and is not currently in widespread use.
History[edit]
Metfendrazine was first synthesized in the 1960s, around the same time as its better-known relative, phenmetrazine. Both drugs were developed as potential treatments for conditions such as obesity, narcolepsy, and ADHD. However, phenmetrazine was found to have a high potential for abuse and was eventually banned in many countries. Metfendrazine, on the other hand, has not been as widely studied or used.
Pharmacology[edit]
Like other stimulant drugs, metfendrazine works by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. These include dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, which are involved in regulating mood, energy levels, and attention. However, the exact mechanism of action of metfendrazine is not fully understood.
Potential Uses[edit]
While metfendrazine is not currently approved for any medical uses, it has been studied as a potential treatment for conditions such as obesity and ADHD. However, more research is needed to determine its efficacy and safety for these uses.
Side Effects and Risks[edit]
As a stimulant, metfendrazine can have a number of side effects. These may include insomnia, increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and anxiety. There is also a risk of dependence and abuse, similar to other stimulant drugs.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of metfendrazine varies by country. In some places, it is classified as a controlled substance, while in others it is not regulated.
See Also[edit]
-
Metfendrazine