Vinbarbital: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A barbiturate derivative used as a sedative and hypnotic}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002123 | |||
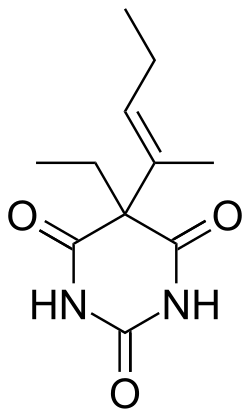
| image = Vinbarbital_skeletal.svg | |||
| image_size = 200px | |||
| image_alt = Skeletal structure of Vinbarbital | |||
}} | |||
'''Vinbarbital''' is a [[barbiturate]] derivative that has been used primarily as a [[sedative]] and [[hypnotic]]. It is a [[central nervous system]] [[depressant]] that works by enhancing the effects of the [[neurotransmitter]] [[gamma-aminobutyric acid]] (GABA) at the [[GABA_A receptor]]. | |||
Vinbarbital | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Vinbarbital, like other barbiturates, acts on the [[central nervous system]] to produce a range of effects from mild sedation to full anesthesia. It enhances the inhibitory effects of [[GABA]], leading to increased [[chloride ion]] conductance and hyperpolarization of neurons. | |||
== | ==Medical uses== | ||
Vinbarbital has been used in the past for its sedative and hypnotic properties. It was prescribed to treat [[insomnia]], [[anxiety]], and sometimes used as a [[pre-anesthetic]] agent. | |||
==Side effects== | |||
Common side effects of vinbarbital include [[drowsiness]], [[dizziness]], and [[ataxia]]. Long-term use can lead to [[tolerance]], [[dependence]], and [[withdrawal]] symptoms upon cessation. | |||
== | ==History== | ||
Vinbarbital was developed in the early 20th century as part of the class of [[barbiturates]], which were widely used before the advent of [[benzodiazepines]]. | |||
==Chemical structure== | |||
[[File:Vinbarbital_skeletal.svg|thumb|right|200px|Skeletal structure of Vinbarbital]] | |||
Vinbarbital is chemically related to other barbiturates, sharing the core structure of a [[barbituric acid]] derivative with modifications that affect its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Barbiturate]] | * [[Barbiturate]] | ||
* [[Sedative]] | * [[Sedative]] | ||
* [[Hypnotic]] | * [[Hypnotic]] | ||
* [[ | * [[GABA_A receptor]] | ||
[[Category:Barbiturates]] | [[Category:Barbiturates]] | ||
[[Category:Sedatives]] | [[Category:Sedatives]] | ||
[[Category:Hypnotics]] | [[Category:Hypnotics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:46, 15 February 2025
A barbiturate derivative used as a sedative and hypnotic
| Vinbarbital | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Vinbarbital is a barbiturate derivative that has been used primarily as a sedative and hypnotic. It is a central nervous system depressant that works by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABA_A receptor.
Pharmacology[edit]
Vinbarbital, like other barbiturates, acts on the central nervous system to produce a range of effects from mild sedation to full anesthesia. It enhances the inhibitory effects of GABA, leading to increased chloride ion conductance and hyperpolarization of neurons.
Medical uses[edit]
Vinbarbital has been used in the past for its sedative and hypnotic properties. It was prescribed to treat insomnia, anxiety, and sometimes used as a pre-anesthetic agent.
Side effects[edit]
Common side effects of vinbarbital include drowsiness, dizziness, and ataxia. Long-term use can lead to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
History[edit]
Vinbarbital was developed in the early 20th century as part of the class of barbiturates, which were widely used before the advent of benzodiazepines.
Chemical structure[edit]

Vinbarbital is chemically related to other barbiturates, sharing the core structure of a barbituric acid derivative with modifications that affect its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties.