Trustee: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Trusts in Medicine == | |||
[[File:Chart_of_a_trust.jpg|thumb|right|Diagram illustrating the structure of a trust.]] | |||
A '''trust''' in the context of [[medicine]] refers to a legal arrangement where one party, known as the [[trustee]], holds and manages assets for the benefit of another party, known as the [[beneficiary]]. Trusts are commonly used in healthcare to manage funds for medical research, patient care, and other health-related purposes. | |||
== Types of Trusts in Healthcare == | |||
Trusts in healthcare can be categorized into several types, each serving different purposes: | |||
== | === Charitable Trusts === | ||
Charitable trusts are established to support [[non-profit]] organizations, including hospitals and research institutions. These trusts provide funding for medical research, patient care, and community health programs. | |||
=== Special Needs Trusts === | |||
Special needs trusts are designed to provide for individuals with disabilities without affecting their eligibility for government benefits. These trusts ensure that beneficiaries receive the necessary medical care and support services. | |||
=== Health Savings Trusts === | |||
Health savings trusts are used to manage funds set aside for future medical expenses. These trusts can be beneficial for individuals planning for long-term healthcare needs. | |||
== Role of Trustees == | |||
The [[trustee]] plays a crucial role in managing the trust's assets. Trustees are responsible for: | |||
* Ensuring that the trust's assets are used according to the terms set forth in the trust agreement. | |||
* Making investment decisions to grow the trust's assets. | |||
* Distributing funds to beneficiaries as needed for medical expenses or other specified purposes. | |||
== Benefits of Trusts in Medicine == | |||
Trusts offer several benefits in the medical field, including: | |||
* '''Financial Security:''' Trusts provide a secure way to manage and allocate funds for healthcare needs. | |||
* '''Tax Advantages:''' Certain types of trusts offer tax benefits, which can be advantageous for both donors and beneficiaries. | |||
* '''Flexibility:''' Trusts can be tailored to meet specific healthcare needs and goals. | |||
== Challenges and Considerations == | |||
While trusts offer many benefits, there are also challenges to consider: | |||
* '''Complexity:''' Setting up and managing a trust can be complex and may require legal and financial expertise. | |||
* '''Costs:''' There are costs associated with establishing and maintaining a trust, including legal fees and trustee compensation. | |||
* '''Regulatory Compliance:''' Trusts must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, which can vary by jurisdiction. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Healthcare finance]] | |||
* [[Medical ethics]] | |||
* [[Non-profit organization]] | |||
* [[Disability rights]] | |||
[[Category:Healthcare]] | |||
[[Category:Legal terms]] | [[Category:Legal terms]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:47, 13 February 2025
Trusts in Medicine[edit]
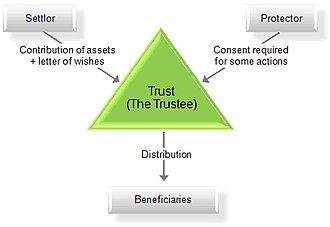
A trust in the context of medicine refers to a legal arrangement where one party, known as the trustee, holds and manages assets for the benefit of another party, known as the beneficiary. Trusts are commonly used in healthcare to manage funds for medical research, patient care, and other health-related purposes.
Types of Trusts in Healthcare[edit]
Trusts in healthcare can be categorized into several types, each serving different purposes:
Charitable Trusts[edit]
Charitable trusts are established to support non-profit organizations, including hospitals and research institutions. These trusts provide funding for medical research, patient care, and community health programs.
Special Needs Trusts[edit]
Special needs trusts are designed to provide for individuals with disabilities without affecting their eligibility for government benefits. These trusts ensure that beneficiaries receive the necessary medical care and support services.
Health Savings Trusts[edit]
Health savings trusts are used to manage funds set aside for future medical expenses. These trusts can be beneficial for individuals planning for long-term healthcare needs.
Role of Trustees[edit]
The trustee plays a crucial role in managing the trust's assets. Trustees are responsible for:
- Ensuring that the trust's assets are used according to the terms set forth in the trust agreement.
- Making investment decisions to grow the trust's assets.
- Distributing funds to beneficiaries as needed for medical expenses or other specified purposes.
Benefits of Trusts in Medicine[edit]
Trusts offer several benefits in the medical field, including:
- Financial Security: Trusts provide a secure way to manage and allocate funds for healthcare needs.
- Tax Advantages: Certain types of trusts offer tax benefits, which can be advantageous for both donors and beneficiaries.
- Flexibility: Trusts can be tailored to meet specific healthcare needs and goals.
Challenges and Considerations[edit]
While trusts offer many benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
- Complexity: Setting up and managing a trust can be complex and may require legal and financial expertise.
- Costs: There are costs associated with establishing and maintaining a trust, including legal fees and trustee compensation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Trusts must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements, which can vary by jurisdiction.