Suboccipital triangle: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Suboccipital_triangle_dissection_-_Suboccipital_triangle.png|Dissection of the Suboccipital Triangle | |||
File:Suboccipital_triangle11.png|Suboccipital Triangle | |||
File:Suboccipital_triangle_-_animation01.gif|Animation of the Suboccipital Triangle | |||
File:Suboccipital_triangle_-_animation03.gif|Animation of the Suboccipital Triangle | |||
File:Suboccipital_triangle.PNG|Suboccipital Triangle | |||
File:Gray563.png|Anatomy of the Suboccipital Triangle | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:02, 18 February 2025
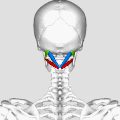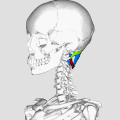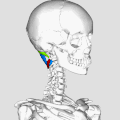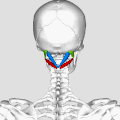
Suboccipital Triangle
The Suboccipital Triangle is a region of the human body found in the neck. It is a significant anatomical feature due to its relationship with various muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
Anatomy[edit]
The Suboccipital Triangle is bordered by three muscles: the Rectus capitis posterior major, the Obliquus capitis superior, and the Obliquus capitis inferior. These muscles are part of the suboccipital group of muscles that contribute to movements of the head at the atlanto-occipital joint.
The floor of the Suboccipital Triangle is formed by the posterior atlanto-occipital membrane and the posterior arch of the atlas.
Contents[edit]
The Suboccipital Triangle contains the vertebral artery and the suboccipital nerve. The vertebral artery supplies blood to the posterior part of the brain, while the suboccipital nerve provides sensory and motor innervation to the muscles in the suboccipital region.
Clinical significance[edit]
Due to its location and the vital structures it contains, the Suboccipital Triangle is of clinical importance. Conditions such as vertebral artery syndrome and occipital neuralgia can be related to this region.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
- Suboccipital Triangle at WikiMD