Pyloromyotomy: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Pyloromyotomy == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Pyloric_Stenosis.png|Pyloric Stenosis | |||
File:PyloricStenosisHorizontal.jpg|Pyloromyotomy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:57, 18 February 2025
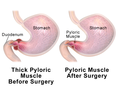
Pyloromyotomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat pyloric stenosis, a condition that causes severe vomiting in the first few months of life. Pyloric stenosis is a condition that affects the gastrointestinal tract during infancy, causing the pylorus to thicken and narrow, which leads to food being blocked from entering the small intestine.
Symptoms of Pyloric Stenosis[edit]
The symptoms of pyloric stenosis usually appear within three to five weeks after birth and may include the following:
- Vomiting: This is often described as "projectile" because it can be forceful enough to project several feet away.
- Weight loss and dehydration: Due to the repeated vomiting, babies with pyloric stenosis can lose weight and become dehydrated.
- Changes in stool: Babies with this condition may have fewer and smaller stools because less food is reaching the intestines.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of pyloric stenosis involves a physical examination and imaging tests. The doctor may feel a small lump in the baby's abdomen. Ultrasound is the most common imaging test used to diagnose this condition. It can show the thickened muscle and the narrowed opening of the pylorus.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for pyloric stenosis is a surgical procedure called a pyloromyotomy. This procedure involves cutting the thickened muscle of the pylorus to allow food to pass into the small intestine. The surgery is usually performed using minimally invasive techniques, which involve making small incisions and using special surgical instruments.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for babies who have a pyloromyotomy is generally excellent. Most babies are able to start eating within a few hours after surgery and can often go home within a day or two. Complications are rare but can include infection, bleeding, and damage to the intestines.