Rocket: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Soyuz TMA-9 launch.jpg|Soyuz TMA-9 launch | |||
File:Oldest depiction of rocket arrows.jpg|Oldest depiction of rocket arrows | |||
File:Rocket warfare.jpg|Rocket warfare | |||
File:William Congreve at Copenhagen 1807.jpg|William Congreve at Copenhagen 1807 | |||
File:Goddard and Rocket.jpg|Goddard and Rocket | |||
File:RIAN archive 303890 A battery of Katyusha during the 1941-1945 Great Patriotic War.jpg|A battery of Katyusha during the 1941-1945 Great Patriotic War | |||
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 141-1880, Peenemünde, Start einer V2.jpg|Peenemünde, Start einer V2 | |||
File:Apollo 15 launch.ogv|Apollo 15 launch | |||
File:Viking 5C rocketengine.jpg|Viking 5C rocket engine | |||
File:Gas Core light bulb.png|Gas Core light bulb | |||
File:Pendulum rocket fallacy.png|Pendulum rocket fallacy | |||
File:Trident II missile image.jpg|Trident II missile | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:25, 20 February 2025
Rocket
A rocket is a vehicle, spacecraft, aircraft or other device that obtains thrust from a rocket engine. Rocket engine exhaust is formed entirely from propellant carried within the rocket. Rocket engines work by action and reaction and push rockets forward simply by expelling their exhaust in the opposite direction at high speed, and can therefore work in the vacuum of space.
History[edit]
The earliest rockets were used as propulsion systems for arrows, and may have appeared as early as the 10th century in Song Dynasty China. The technology gradually spread to the Middle East, Europe, and other regions. Rockets became a significant tool during the 20th century, particularly in World War II, the Cold War, and the Space Age, where they were used in early ballistic missiles and space exploration.
Principle of operation[edit]
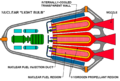
Rockets create thrust by expelling mass backwards in a high-speed stream. This follows Newton's third law of motion. A rocket, unlike a jet engine, carries everything it needs for propulsion. This allows it to operate in the vacuum of space.
Types of rockets[edit]
There are many different types of rockets, and a comprehensive list can be found at List of rockets. Some of the more commonly known types include the Saturn V, which was used in the Apollo moon missions, and the Space Shuttle.
See also[edit]
- Rocket (disambiguation)
- Rocket engine
- Rocket launch
- Rocket propellant
- Rocket sled
- Rocket sonde
- Rocket stove
- Rocket vehicle
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
|
|
|
-
Soyuz TMA-9 launch
-
Oldest depiction of rocket arrows
-
Rocket warfare
-
William Congreve at Copenhagen 1807
-
Goddard and Rocket
-
A battery of Katyusha during the 1941-1945 Great Patriotic War
-
Peenemünde, Start einer V2
-
Apollo 15 launch
-
Viking 5C rocket engine
-
Gas Core light bulb
-
Pendulum rocket fallacy
-
Trident II missile