Pyroptosis: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
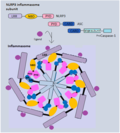
File:Inflammasome final1.png|Pyroptosis | |||
File:Pyroptosis pathways 2.png|Pyroptosis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:38, 20 February 2025
Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death that occurs most frequently upon infection with intracellular pathogens and is a component of the antimicrobial response. This process promotes the rapid clearance of various bacterial and viral infections by removing intracellular replication niches and enhancing the host's defensive responses.
Mechanism[edit]
The process of pyroptosis is mediated by certain members of the caspase family. These enzymes are activated by various pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Once activated, these caspases cleave a protein called gasdermin D, the active form of which can form pores in the cell membrane, leading to cell swelling and eventual rupture.
Role in disease[edit]
Pyroptosis has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including sepsis, stroke, and heart attack. It also plays a role in certain autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. In addition, it has been suggested that pyroptosis may play a role in certain neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Therapeutic potential[edit]
Given its role in various diseases, there is interest in developing drugs that can modulate the process of pyroptosis. For example, inhibitors of the caspases that mediate pyroptosis are being investigated for their potential to treat sepsis and other inflammatory diseases.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />